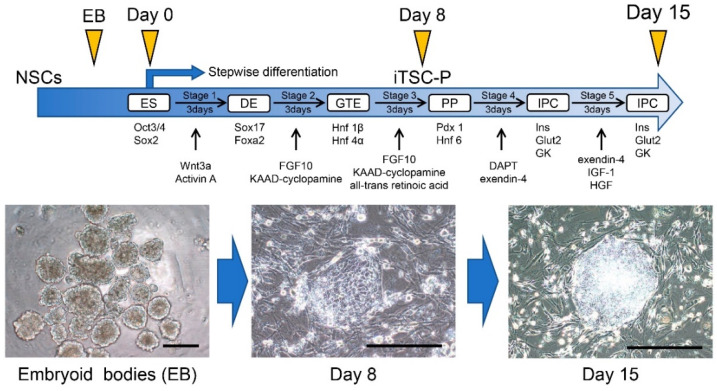
Figure 4.
The new protocol enabling the differentiation of HDDPC-NSCs into pancreatic β-cells. The schedule for the in vitro differentiation of HDDPC-NSCs, shown in the upper panel, is adapted from Kiyokawa et al. [64], MDPI, 2020. After formation of embryoid bodies (EB) from HDDPC-NSCs, the resultant EBs were seeded onto a tissue-culture dish to them to promote outgrowth for 2 days. Next, these cells were subjected to a stepwise protocol to drive differentiation toward IPCs (upper panel). In Stage 1, the cells were treated with Wnt3a and activin A for 1 day, followed by treatment with activin A + 0.2% FBS for 2 days. In Stage 2, the cells were treated with fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and 3-keto-N-(aminoethyl-aminocaproyl-dihydrocinnamoyl) cyclopamine (KAAD-cyclopamine) + 2% FBS for 3 days. In Stage 3, the cells were treated with FGF10, KAAD-cyclopamine, and all-trans retinoic acid + 1% (vol/vol) B27 supplement for 3 days. In Stage 4, the cells were treated with N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl)-l-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester (DAPT) and exendin-4 + 1% (vol/vol) B27 supplement for 3 days. In Stage 5, the cells were treated with exendin-4, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and hepatocyte growth factor + 1% (vol/vol) B27 supplement for 3–6 days. The resultant iTS-P cells were continuously maintained in NSC medium on feeder layers of MMC-treated MEF cells. In the lower panel, photographs show the differentiation process from embryoid bodies into intermediate cells that expressed PDX1 and were capable of producing insulin. We obtained these images from experiments performed exclusively for this review. Scale = 200 μm. ES, embryonic stem; DE, definitive endoderm; GTE, gut tube endoderm; PP, pancreatic progenitors; IPC, insulin-producing cell; PDX1, pancreatic-duodenal homeobox factor-1; EB, embryoid bodies.