Figure 1.
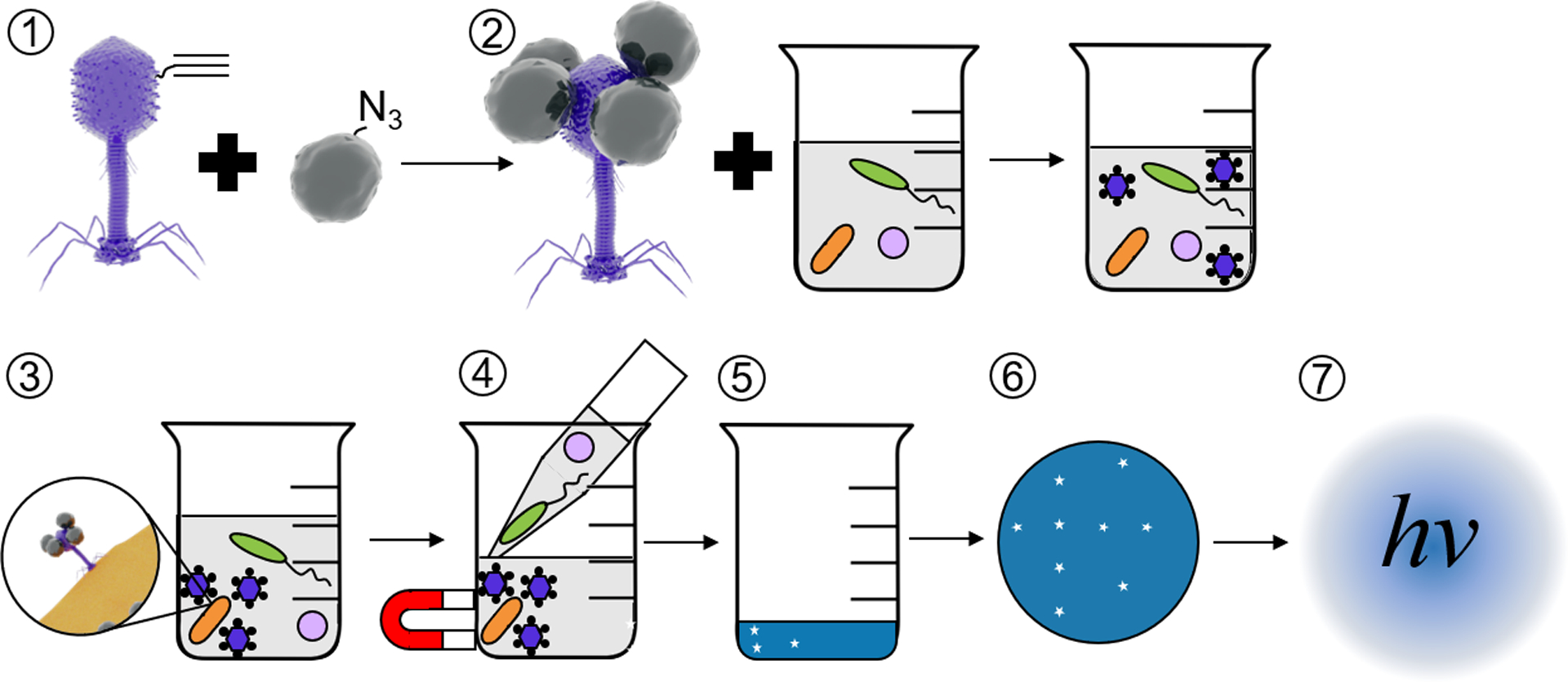
Schematic of E. coli detection assay. Self-assembled alkynylated T4 Nluc CBM phages are conjugated to azide-coated MNPs (1) using click chemistry. The resulting magnetic phage-based bioaffinity nanobot is added to samples of environmental water (2), where the phages bind specifically to E. coli (orange rods, 3). Beads, along with phages and E. coli, are collected with a magnet and excess volume is aspirated (4). Infection cycle completes (5), releasing Nluc CBM into solution. Samples are filtered (6) on cellulose to immobilize Nluc CBM and luminescence is measured (7) to detect E. coli. Please note that the schematics in this figure are not to scale. T4 Nluc CBM is approximately 200 nm long and 900 nm in diameter. MNPs are approximately 15 nm in diameter (Table S9).
