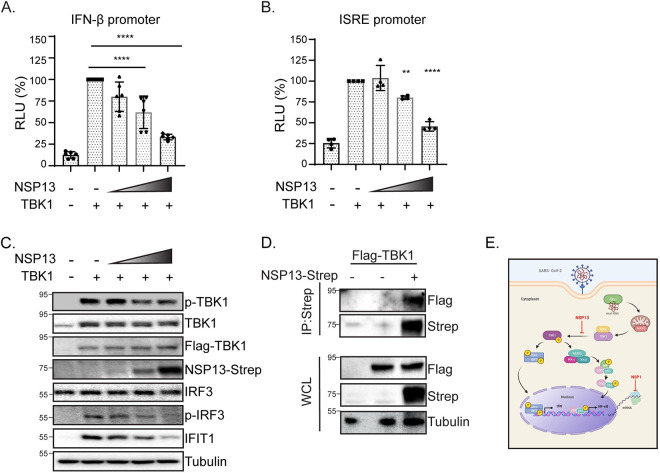
Fig 4. SARS-CoV-2 protein NSP13 interacts with TBK1 and blocks TBK1-mediated IFN activation.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of anti-Strep immunoprecipitated lysates or whole cell lysate (WCL) of 293T cells transfected with Flag-TBK1 or co-transfected with Flag-TBK1 and NSP13-Strep. Actin was used as a loading control and ladder is displayed in kDa. (B). IFN-β-promoter driven luciferase activity of HeLa cells expressing TBK1 and varying amounts of SARS-CoV-2 NSP13 protein for 24 hours. Values depict mean ± SD (n = 6 biological replicates) in relative luciferase units (RLU). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (C) ISRE-promoter driven luciferase activity of HeLa cells expressing TBK1 and varying amounts of SARS-CoV-2 NSP13 protein for 24 hours. Values depict the mean ± SD (n = 4 biological replicates) in relative luciferase units (RLU). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (D) Immunoblot analysis of lysates harvested at 24 hours from HeLa cells transfected with TBK1 and varying amounts of SARS-CoV-2 NSP13. Tubulin is shown as a loading control. Ladder is included as kDa. (E) Schematic depicting the TBK1 pathway and effect of SARS-CoV-2 NSP1 and NSP13 on NF-κB activation and IFN-β activation. During RNA virus infection, viral RNA is recognized and bound by cytosolic recognition receptors, such as RIG-I. This binding initiates a downstream signaling cascade through the protein adaptor MAVS, which interacts with the kinases IKKε and TBK1. TBK1 phosphorylation initiates two branches of signaling: (1) dimerization and phosphorylation of the transcription factor IRF3 and (2) recruitment to a complex with the signaling molecules NEMO, IKK-α and IKK-β, subsequent phosphorylation and degradation of the inhibitor of κB (IκB), and phosphorylation of the p65 subunit of the transcription factor NF-κB. Phosphorylation of these two transcription factors results in their nuclear translocation, where they can bind to the promoters of type I IFNs and pro-inflammatory cytokines. NSP13 is shown with an inhibitory arrow at the level of TBK1 activation. NSP1 is shown with an inhibitory arrow at the level of host mRNA translation. This schematic was created using BioRender.com.