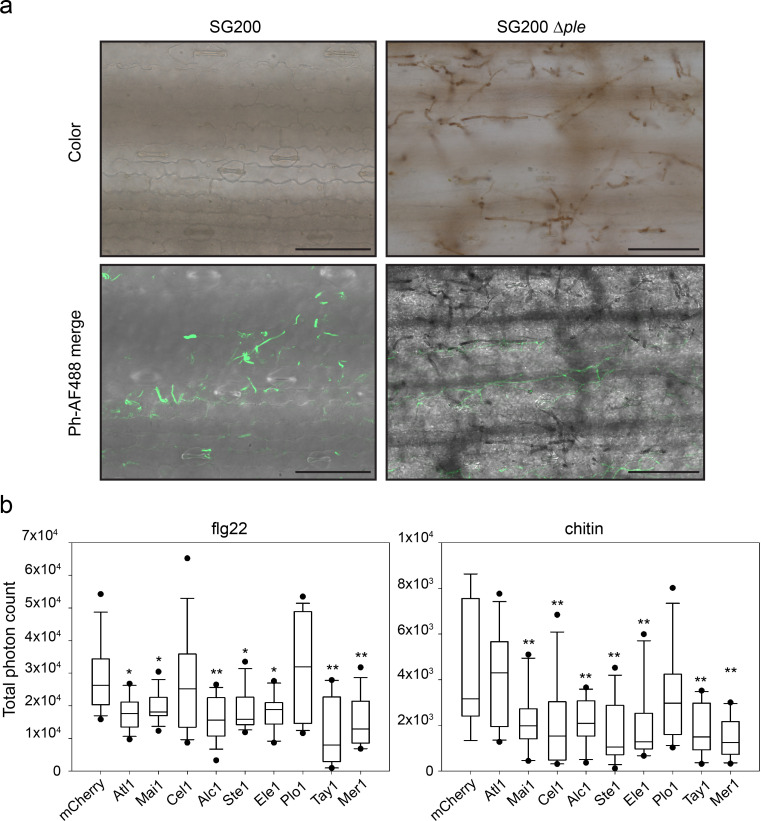
Fig 2. Pleiades contribute to the suppression of early defense responses.
a. Accumulation of H2O2 in infected leaves visualized by diamino benzidine (DAB) staining. Left panels: U. maydis SG200 colonizes the host tissue without showing strong DAB precipitation. Right panels: U. maydis SG200 Δple shows pronounced precipitation of DAB around the hyphae upon colonization of the host. Upper panels: color pictures showing the brown DAB precipitate. Lower panels: Phase contrast/Alexa Fluor 488 merge. WGA-Alexa Fluor 488 (which binds chitin) was used as a counter stain to show the presence of hyphae not stained by DAB since the precipitate covers and mask chitin from being bound by WGA. Samples were collected 36h post infection. Scale bar = 100 μm. Color pictures and the Fluorescent/Phase contrast pictures are taken with different cameras; therefore, the fields of the upper and lower panels don’t overlay perfectly. b. PAMP-triggered ROS burst in N. benthamiana. Transient expression of pleiades (without their predicted secretion signal) leads to reduction of the oxidative burst triggered by flg22 (left) or chitin (right). Plants expressing mCherry were used as the reference control. Total photon counts over 40 (flg22) or 30 minutes (chitin) are shown as box plots. Data is a pool of three (flg22) or four (chitin) independent experiments, n = 15 or 12 plants respectively. Significant differences between proteins were analyzed by ANOVA with Benjamini-Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01).