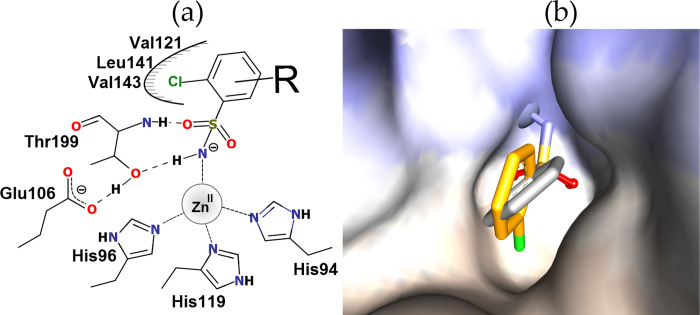
Fig 1. The interactions between CA II and the 2-chlorobenzenesulfonamide-bearing compound.
Panel (a): The negatively charged amino group of the sulfonamide forms a coordination bond with the Zn(II) in the active site and prevents the CO2 substrate binding. Additional R substituents form hydrophobic and other contacts with the protein amino acids. Panel (b): The chlorine (green) of the 2-chloro-benzenesulfonamide (orange) occupies the binding site cavity and orients the compound in the active site of CA II as compared to the benzenesulfonamide (grey) (PDB IDs 2WEH and 2WEJ [10]).