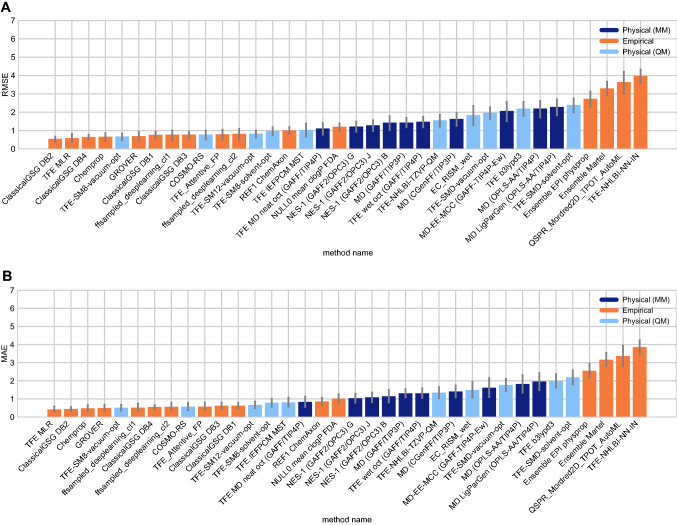
Fig. 4.
Overall accuracy assessment for all methods participating in the SAMPL7 log P challenge shows that many methods did not exhibit statistically significant differences in performance and there was no single clear winner; however, empirical methods tended to perform better in general. Both root-mean-square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) are shown, with error bars denoting 95% confidence intervals obtained by bootstrapping over challenge molecules. Empirical methods outperform the majority of the other methods. Methods that achieved a RMSE 1.0 log P units were mainly empirical based, and some were QM-based physical methods. Submitted methods are listed in Table 1. The submission REF1 ChemAxon [80] was a reference method included after the blind challenge submission deadline, and NULL0 mean cLogP FDA is the null prediction method; all others refer to blind predictions