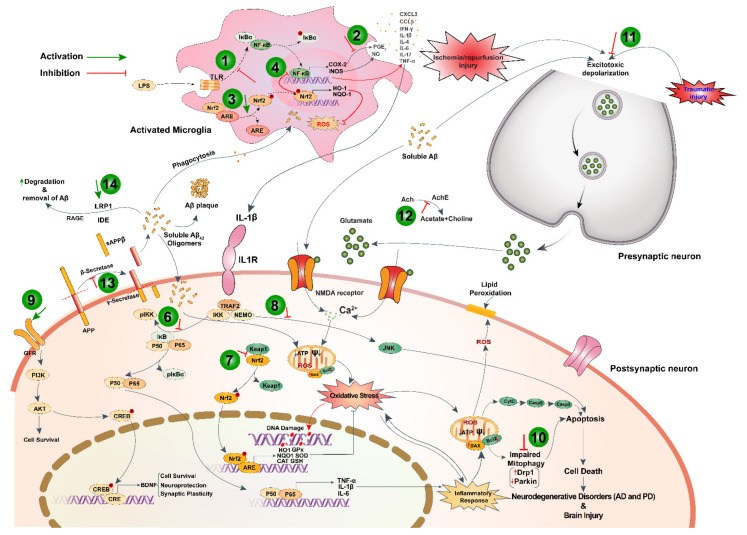
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram illustrating the pathobiology of degenerative brain disorders and post-ischemic/traumatic consequences showing point of action of black cumin and TQ. The neuroprotective mechanisms of black cumin and TQ involve (1) attenuation of inflammatory response via inhibition of NF-κB signaling; (2) inhibition of COX-2 activity; (3) induction of antioxidant defense system via activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway; (4) cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB; and (5) attenuation of oxidative stress in activated microglia; (6) protection against neuroinflammation by inhibiting NF-κB signaling; (7) priming of antioxidant defense system by activating Nrf2/ARE pathway; (8) prevention of apoptosis via downregulating pro-apoptotic JNK/Erk pathway; (9) activation of BDNF-dependent pro-survival pathway via inducing PI3K/Akt signaling; and (10) induction of mitophagy in neuron; (11) attenuation of I/R-injury via preventing excitotoxic depolarization in presynaptic terminal of neuron; (12) anticholinesterase activity; (13) anti-amyloidogenesis via blocking β-secretase activity; and (14) Aβ-clearance by upregulating IDE, LRP1, and RAGE. TLR, toll-like receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF-κB (p50-p65), nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ARE, antioxidant response element; IkB, inhibitor of NF-κB; IKK, IκB kinase; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; COX2, cyclooxygenase 2; iNOS, inducible isoform of Nitric oxide synthase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; NQO-1, NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; NO, nitric oxide; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL1R, interleukin-1 receptor; APP, amyloid precursor protein; LRP1; Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; IDE, insulin-degrading enzyme; RAGE, Receptor for advanced glycation end-products; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; GluN2B, N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; GFR, growth factor receptor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; Akt, protein kinase B; CREB, cAMP-response element binding protein; BDNF, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Drp1; dynamin-related protein-1; AChE, acetylcholinesterase; Ach, acetylcholine; ψ, mitochondrial membrane potential. This image is modified from [88].