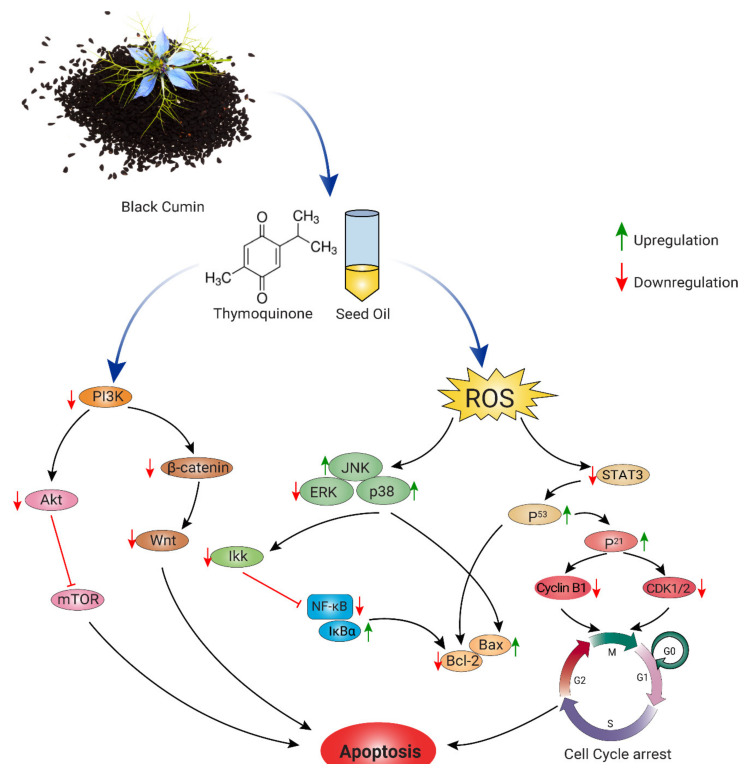
Figure 4.
Plausible anticancer mechanism of black cumin, TQ, and essential oil: triggering cellular apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Black cumin and its components provoked cancer-cell specific apoptosis via altering several signaling cascades, including PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Wnt/β-catenin, and NF-κB signaling. Black cumin and its components also caused DNA damage that involves several mechanisms such as ROS induction and subsequent increase in oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction which eventually increase Bax/Bcl-2 ratio through c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) pathway. Black cumin also suppressed Cyclin B1 and CDK1/2 expression through regulating STAT3 and MAPK pathways and caused cell cycle arrest. ROS, reactive oxygen species; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription-3; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; CDK1/2, cyclin-dependent kinase 1/2; Cyclin B1, regulatory protein of maturation-promoting factor.