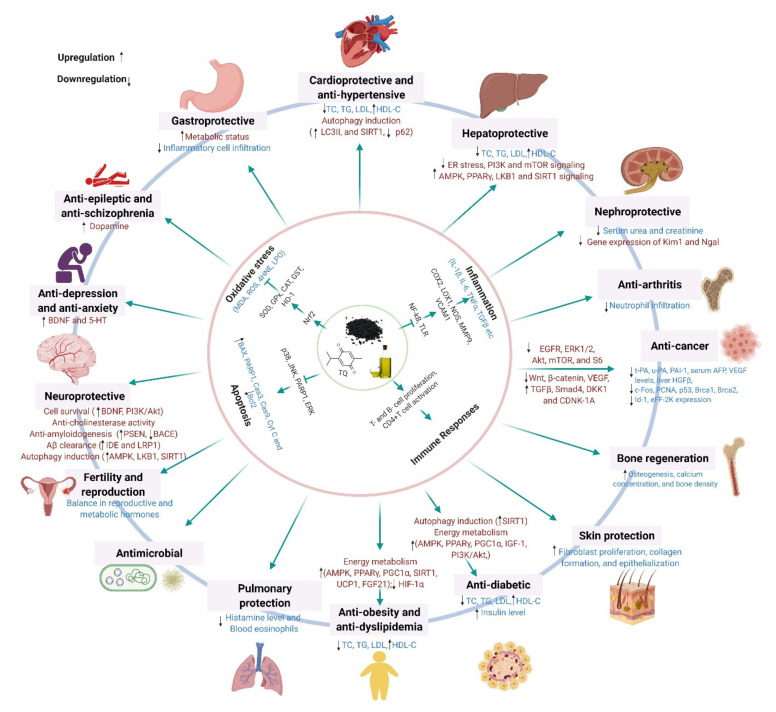
Figure 6.
Comprehensive molecular mechanism of black cumin and TQ-mediated pharmacological actions. The general pharmacological effects are manifested by their capacity to attenuate oxidative stress by activating the antioxidant defense system (Nrf2 signaling), inhibit inflammation by activating anti-inflammatory signaling (NF-κB and TLR signaling), induce immunity by modulating innate and adaptive immune components, prevent apoptosis by upregulating pro-survival signals and downregulating pro-apoptotic signals (PI3K/Akt, JNK, and mTOR signaling). Other significant molecular mechanisms include induction of autophagy (SIRT1 signaling), priming of energy metabolism (AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1α and PPARγ signaling), activation of growth factor signaling (PI3K/Akt signaling), and enhancement of protein clearance by upregulating LRP1. Through employing multiple of these pharmacological mechanisms, black cumin and TQ exerted their health benefits including protection against metabolic (obesity, dyslipidemia, and diabetes), cardiovascular, digestive, renal, hepatic, osteogenic, respiratory, reproductive, neurological and mental disorders, and various types of cancer.