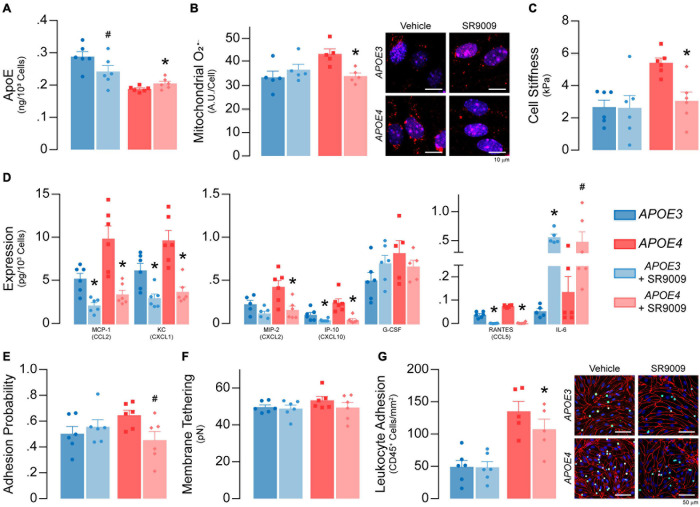
FIGURE 10.
SR9009 treatment impacts metabolism and inflammation in APOE4 brain endothelial cells. At confluence, brain endothelial cells were treated with 5 μM SR9009 for the 48 h leading up to each assay. (A) SR9009 treatment results in lower apoE levels (∼16%) with APOE3 and higher levels (∼9%) with APOE4 when assessed by ELISA. (B) SR9009-treated APOE4, but not APOE3, brain endothelial cells have lower mitochondrial superoxide levels compared to the vehicle (n = 5). (C) Cell stiffness is lower in SR9009-treated APOE4, but not in APOE3, brain endothelial cells (analyzed by paired t-test). (D) MCP-1/CCL2, KC/CXCL1, IP-10/CXCL10 and RANTES/CCL5 levels are lower with SR9009 in both APOE3 and APOE4 brain endothelial cells when assessed by multiplex ELISA. SR9009 lowers MIP-2 levels in APOE4 brain endothelial cells and increases IL-6 levels for both APOE3 and APOE4 endothelial cells. (E) The adhesion probability is lower in APOE4 brain endothelial cells with SR9009 treatment but (F) membrane tethering force is unaffected (analyzed by paired t-test). (G) Leukocyte adhesion is lower with APOE4 following treatment with SR9009 (APOE3 n = 6, APOE4 n = 5). Data is expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed Student’s t-test and #p < 0.05 by one-tailed Student’s t-test compared to vehicle control with n = 6 (unless otherwise specified above).