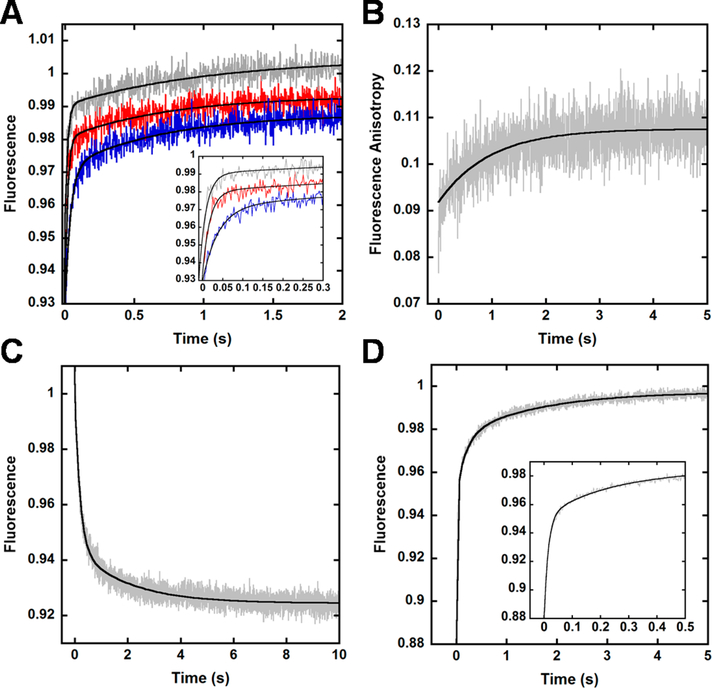
Figure 4.
Conformational changes in the Finger domain upon DNA binding. (A) Dpo4 Finger mutant S22W-V62CCPM (100 nM) was rapidly mixed with varying concentrations of DNAOH (from 20 to 200 nM, from blue to gray traces, respectively), and the CPM fluorescence was monitored upon excitation at 290 nm. The black line depicts a double-exponential fit to the data, and the inset highlights the concentration dependence of the initial fast rate. (B) wt Dpo4 (500 nM) was rapidly mixed with Alexa488-labeled DNAOH (500 nM), and the change in fluorescence anisotropy was measured upon excitation at 499 nm. The black line depicts a single-exponential fit to the data. (C) CPM fluorescence of S22W-V62CCPM (100 nM) preincubated with DNAOH (100 nM) upon excitation at 290 nm following rapid mixing with a 20-fold excess of wt Dpo4 (2 μM). The black line depicts a double-exponential fit to the data. (D) CPM fluorescence of S22W-V62CCPM (2 μM) was monitored upon excitation at 290 nM following rapid mixing with a preincubated solution of wt Dpo4 (100 nM) and DNAOH (100 nM). The black line depicts a triple-exponential fit to the data, and the inset features the fast time points to illustrate the multiexponential behavior of the data.