Figure 3.
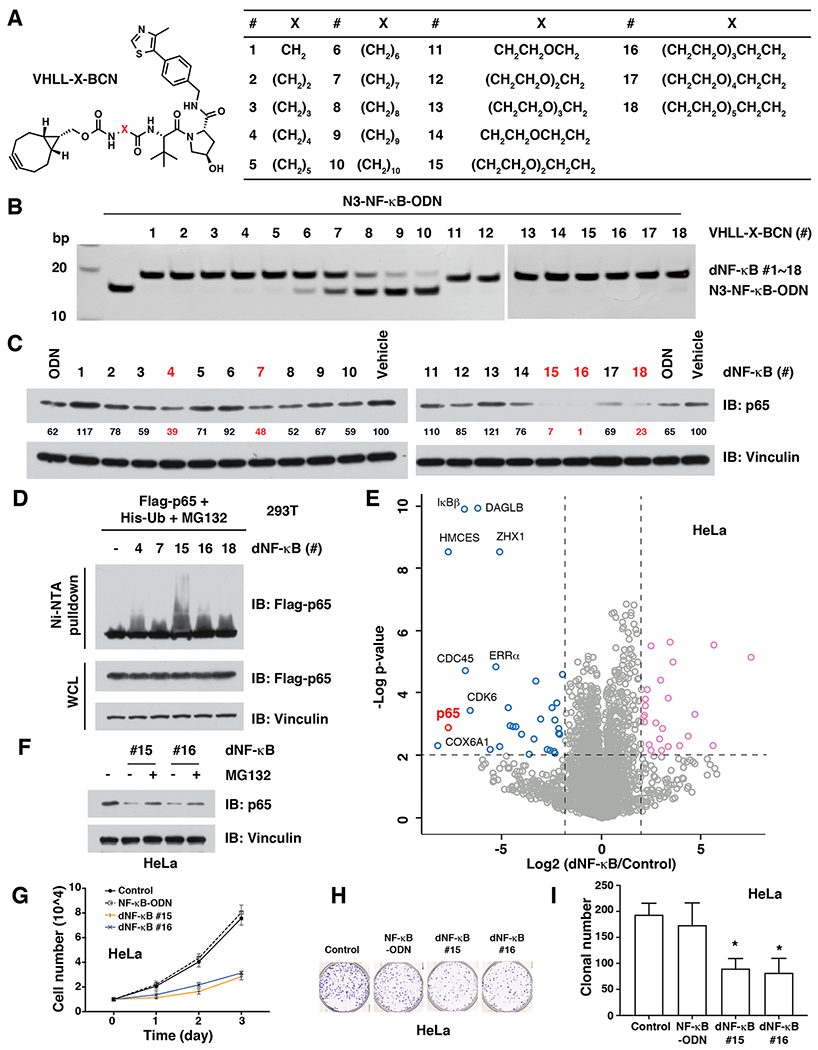
dNF-κB promotes the targeted degradation of the NF-κB transcription factor in cells. (A) Design of a series of 18 BCN-modified VHL ligands with various linkers between BCN and the VHL ligand. (B) In vitro click of VHLL-X-BCN (#1 - #18, 150 μM) with N3-NF-κB-ODN (50 μM), which can be separated by native PAGE. (C) Western blots for p65 in HeLa cells after treated with 10 μg/mL of dNF-κB (#1 - #18) for 12 h. (D) dNF-κB (#4, #7, #15, #16, and #18) led to the ubiquitination of p65 in cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-p65 for 24 h and then transfected with 10 μg/mL of indicated dNF-κB for another 12 h, followed by Western blotting for Flag-p65 in Ni-NTA pulldown and whole cell lysis (WCL). (E) Comparison of proteomic changes after treatment with dNF-κB #16 or control in HeLa cells. Dotted lines indicate either 50% loss or 2-fold increase of the protein level (x axis) and p = 0.01 (y axis). (F) The proteasome inhibitor MG132 blocked the degradation of endogenous p65 by dNF-κB (#15 and #16) in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were transfected with 10 μg/mL of indicated dNF-κB and then treated with 10 μM MG132, followed by Western blotting for p65. (G) dNF-κB (#15 and #16, 10 μ/mL) repressed the proliferation of HeLa cells. (H—I) dNF-κB (#15 and #16, 10 μg/mL) reduced the tumorigenesis of HeLa cells in a colony formation assay. *: p < 0.05.
