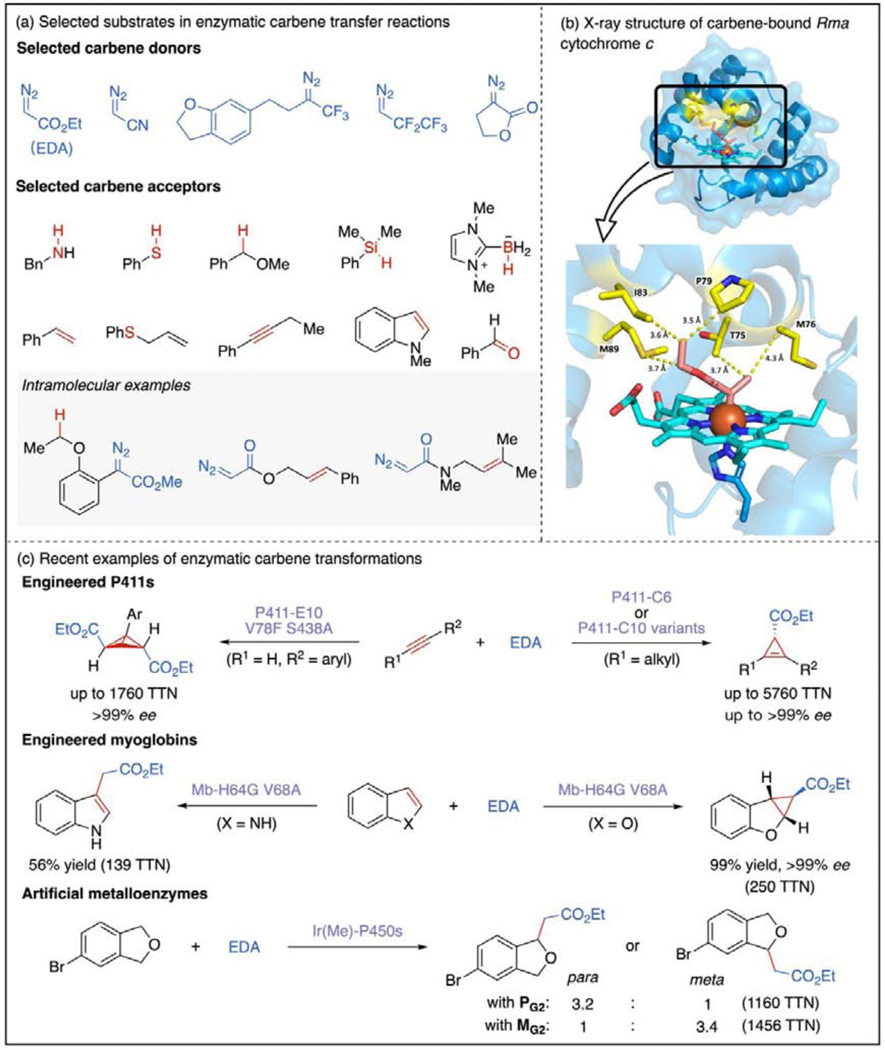
Figure 2.
Hemoprotein-catalyzed carbene transfer reactions. (a) Selected carbene donors and acceptors in enzymatic carbene transfer reactions. All competent carbene donors are diazo compounds bearing an electron-withdrawing group adjacent to the diazo carbon [19–23]. Carbene acceptors range from σ-bonds [19,25,26●] to unsaturated π-systems [24●●,27●●,28]. Intramolecular carbene transfer reactions have also been developed to form ring structures [29●,35]. (b) X-ray crystal structure of carbene-bound Rma cytochrome c (1.29 Å, PDB ID: 6CUN). Hydrophobic amino acid residues interacting with the carbene species are highlighted in yellow [30●]. (c) Recent examples of enzymatic carbene transfer reactions that highlight the evolvability of hemoprotein scaffolds [24●●,27●●,28]. These include challenging transformations catalyzed by artificial metalloenzymes containing exogenously added Ir-porphyrin cofactors [38,39●].