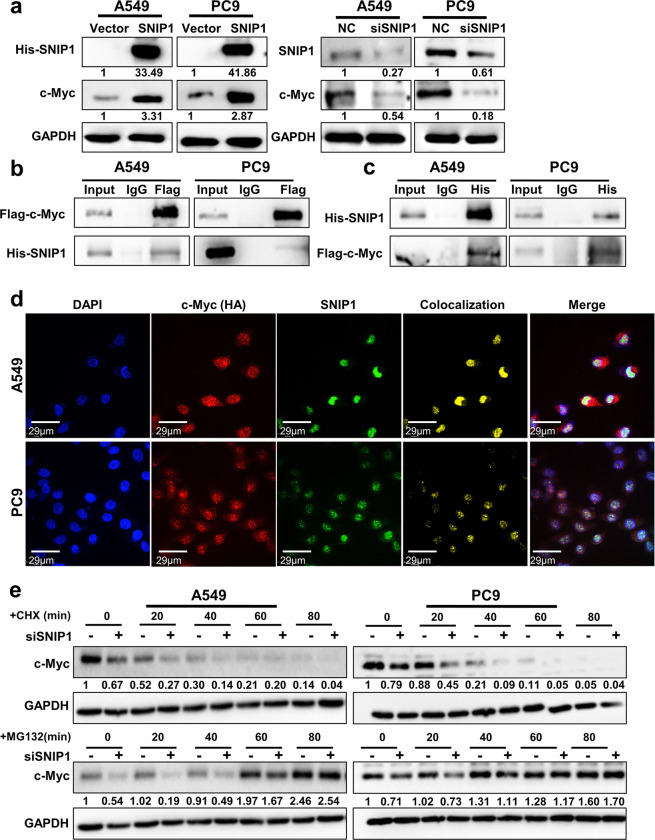
Fig. 5.
SNIP1 inhibits c-Myc protein degradation. a The c-Myc expression in A549 and PC9 cells after knockdown or overexpression of SNIP1 by western blotting. b The interaction between c-Myc and SNIP1 using anti-Flag (c-Myc) antibody in A549 and PC9 cells co-transfected with the Flag-c-Myc and His-SNIP1 vectors was examined by immunoprecipitation. c The interaction between SNIP1 and c-Myc proteins using anti-His (SNIP1) antibody in A549 and PC9 cells co-transfected with the His-SNIP1 and Flag-c-Myc vectors by IP experiment. d Immunofluorescence experiments performed using anti-HA (c-Myc) and anti-SNIP1 antibodies in A549 and PC9 cells showed that c-Myc and SNIP1 were colocalized. DAPI-stained nucleus: blue; anti-HA (c-Myc): red; anti-SNIP1: green; colocalization of c-Myc and SNIP1: yellow; the merged image represents the overlap of DAPI, c-Myc, and SNIP1 (Scale bar: 29 μm). e After knockdown of SNIP1 via transient transfection, A549 and PC9 cells were treated with 50 μg/ml CHX or 20 μM MG132 for 0–80 min, followed by detection of c-Myc protein levels using western blotting method. The results showed that only MG132 abolished the downregulation of c-Myc caused by siSNIP1