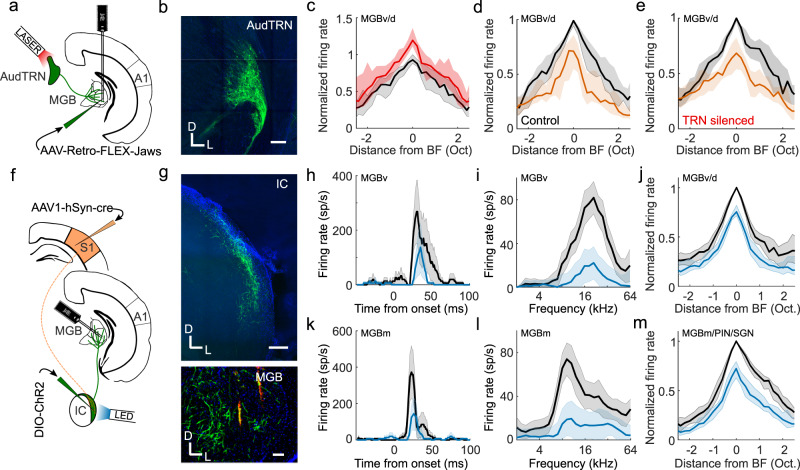
Fig. 7. Corticocollicular circuit mediates somatosensory suppression of the thalamus.
a Schematic of experimental paradigm in b–e. A1, primary auditory cortex; AudTRN, auditory sector of the thalamic reticular nucleus; MGB, medial geniculate body. b GABAergic cells in TRN retrogradely-labeled with Jaws from auditory thalamus. Scale bar, 150 μm. c Summary (median) frequency tuning curves across MGBv/d units with (red) or without (black) optogenetic suppression of AudTRN activity (change in BF firing response, P = 1.1 × 10−6, n = 38, 2 mice, two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test). d, e Median frequency response profile of MGBv/MGBd units (same units as in c) illustrating suppression induced by concurrent whisker stimulation (orange) with AudTRN either unaffected (d) or optogenetically silenced (e). Silencing AudTRN had no overall effect on the whisker-induced suppression of auditory responses in MGBv/MGBd (P = 0.83, n = 38, 2 mice, two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test) and there was no relationship between the change in auditory response magnitude and the effect on whisker-driven suppression of the auditory response (Pearson’s r = −0.055, P = 0.74). f Schematic of experimental paradigm in g–m. g Top: ChR2-YFP expression in neurons in the shell of IC, labeled by anterograde transport of cre from S1 (AAV1-hSyn-cre) and a cre-dependent AAV5-DIO-ChR2-eYFP injected into the IC. Scale bar, 200 μm. Bottom: Axons (green) of anterogradely labeled IC neurons in MGB. Scale bar, 100 μm. Orange marks show DiI tracts from the recording probe in the MGB. D, dorsal; L, lateral. h Example PSTHs illustrating BF responses of an MGBv unit with (blue) and without (black) optogenetic stimulation of S1-recipient IC neurons. i Example frequency response profile of an MGBv unit with (blue) and without (black) optogenetic stimulation of S1-recipient IC neurons. j Median MGBv/MGBd frequency response profile with (blue) and without (black) stimulation of S1-recipient IC neurons: −20.9% median change in BF firing rate (P = 1.4 × 10−14, n = 85, 3 mice, two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test). k–m same as h–j for units recorded in MGBm/PIN/SGN. m −26.9% median change in BF firing rate (P = 3.5 × 10−14; n = 89, 3 mice, two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Shaded area illustrates the s.e.m. (h, k), the 95% confidence intervals of the means (i, l), or the 95% nonparametric confidence intervals of the median (c, d, e, j, m). MGBm/PIN/SGN, MGB medial division/posterior intralaminar nucleus/suprageniculate nucleus; MGBv/d, MGB ventral/dorsal divisions; sp/s, spikes per second.