Table 4.
Examples of US-innovative techniques combinations for the extraction of natural materials.
| Technique | Matrix | Targeted compound | Type of combination | Device diagram | Combination impact | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US combined with mechanical pressing | Sunflower seed | Oil | In line | 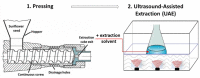 |
US application improved extraction kinetics and oil diffusion from the mass of the cake to the extracting solvent, compared to conventional Soxhlet extraction. | [97] |
| Ultrasound-Microwave Assisted Extraction (UMAE) | Sorghum husk | Natural colorants | Direct in situ (DIS) | 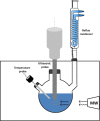 |
Significantly improved extraction yield and better dyeing properties of sorghum husk extracts. | [105] |
| Sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas L.) | Prebiotic oligosaccharides | Direct in situ (DIS) | Higher extraction efficiency compared to theconventional hot-water extraction, microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), and ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) methods. | [106] | ||
| Lotus seed starch-green tea polyphenol complex | Preparation of starch-polyphenol complex | Direct in situ (DIS) | Increased extraction yield of the complex. | [107] | ||
| Potato pulp | Pectin | Direct in situ (DIS) | Increased extraction efficiency of potato pectin. | [107] | ||
| Alternate Microwave/Ultrasound with DES | Schisandra Chinensis fruit | Polysaccharides and essential oil | Alternating US/MW digestion | Higher polysaccharide and essential oils yields. | [109] | |
| Ultrasound Microwave- assisted enzymatic extraction (UMAEE) | Lentinus edodes | Polysaccharides | In line | 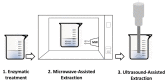 |
Higher extraction yields of polysaccharides content compared to conventional techniques. | [110] |
| Laminaria | Monoiodo-tyrosine (MIT) and Diiodo-tyrosine (DIT) | In line | 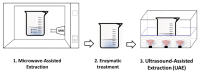 |
An efficient method to extract MIT and DIT from Laminaria. Both US and MW radiation can destroy the laminaria cell walls which improves access and extractability of targeted compounds. | [111] | |
| US combined with pressurized liquid | Sugar beet pulp | Pectin-enriched materials | In line | 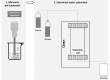 |
Higher extraction yield and improved functional properties obtained with subcritical water extraction. | [112] |
| Pomegranate peel | Phenolic compounds | Direct in situ (DIS) | 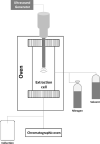 |
Higher extraction yield Reduced extraction time and temperature | [113] | |
| Fragrant oil from red pepper seed | Residual propane | In line | 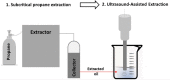 |
US was efficient in solvent residue removal. Treated oil presents good oxidation stability and quality. | [114] | |
| US combined with supercritical CO2 | Agave salmiana bagasse | Antioxidants and saponins | Direct in situ (DIS) | 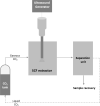 |
Increased extraction yield in terms of antioxidants and saponins contents. | [119] |
| Ginger rhizomes | Pungent compounds | Direct in situ (DIS) | Improved extraction yield of pungent compounds from ginger. | [118] | ||
| Iberis amara seeds | Cucurbitacin E (CuE) | Direct in situ (DIS) | The introduction of ultrasound to supercritical CO2 extraction enhanced CuE yield and reduced operation time as well as the amount of CO2 consumed. | [67] | ||
| Instant controlled pressure drop (DIC) combined with US | Orange peels | Antioxidants | In line | 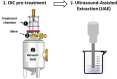 |
The highest yield of antioxidants with best kinetics is obtained by coupling both treatments. | [39] |
| Steviarebaudiana bertoni leaves | Rebaudioside A, Vitamin B6 and vitamin B1. | In line | 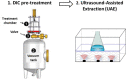 |
DIC pre-treatment has a significant positive effect on the extraction of Rebaudioside A, Vitamin B6 and vitamin B1. | [122] | |
| Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) combined with US | Almond seeds | Phenolics, flavonoids, condensed tannins and anthocyanins, antioxidant activity and volatile compounds | In line | 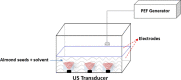 |
Combined treatment (PEF–US) has attained the highest value of total phenolics, total flavonoids, condense tannins, anthocyanin contents and antioxidant activity in DPPH, reducing power and metal chelating activity than all other treatments. | [124] |
| UV-C Radiation Combined with UAE | Cherry Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) | Lycopene | In line | 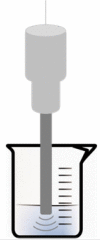 |
Extracted obtained from the irradiated tomatoes presented 5.8 times more lycopene content. | [126] |
| Tomatoes | Bioactive compounds | Direct in situ (DIS) | This postharvest non-thermal treatment resulted in increased lycopene, total phenols, vitamin C, hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant activities during storage. | [125] | ||
| US coupled with CCC and CPC | Paeonia lactiflora Pall roots | Albiflorin, benzoylpaeoniflorin, paeoniflorin, and galloylpaeoniflorin) | In line |  |
The four targeted compounds were successfully extracted. Compared with conventional extraction methods, this combination offers the advantages of automationand systematic extraction and isolation of natural products. | [131] |
