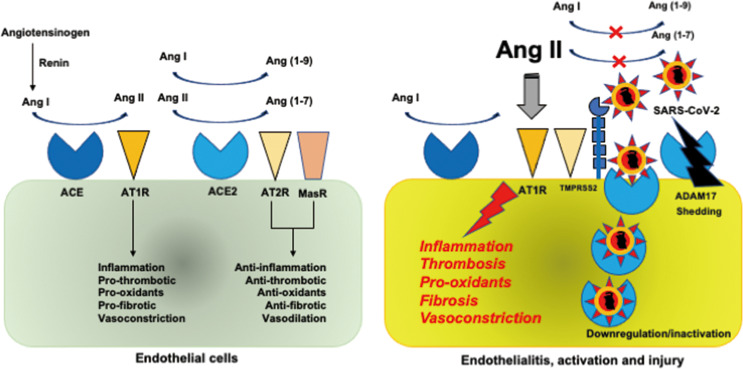
Figure 1.
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. (Left). Renin converts angiotensinogen to Ang I, which is converted to Ang II by ACE. ACE2 degrades Ang I and Ang II to generate Ang(1-9) and Ang(1-7), which have anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic actions through AT2R and MasR. Conversely, Ang II has proinflammatory and prothrombotic properties binding to AT1R and secretes aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. RAAS is balanced by its two opposed properties of inflammation and coagulation by ACE2. (Right). Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 via the spike glycoprotein to TMPRSS2 results in the downregulation and inactivation of ACE2, leading to an increase in Ang II levels, which gives rise to inflammation and thrombosis through AT1R. Proteolysis and shedding of ACE2 resulting from ADAM17 upregulation also contributes to inactivation of ACE2. SARS-CoV-2 infection of endothelial cells causes endothelialitis associated with endothelial activation and injury. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ADAM17, a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain-containing protein 17; Ang, angiotensin; AT1R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; MasR, Mas receptor; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TMPRSS2, transmembrane protease serine type 2.