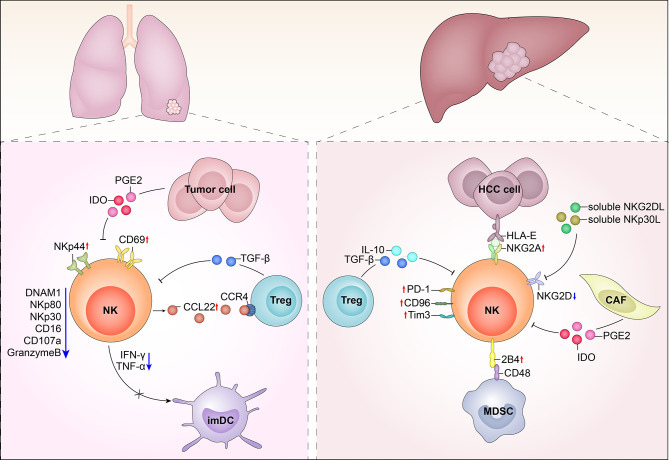
Figure 1.
Tumor infiltrates NK cells in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and lung cancer. Left image: In the tumor microenvironment of lung cancer, NK cells up-regulated the expressions of CD69 and NKp44 and down-regulated the expression of NKp30, NKp80, DNAM-1 and CD16. Series of soluble molecules were secreted by tumor cells, like IDO, PGE2, and TGF-β. Tumor cells also could express membrane molecules that can shed receptors on the surface of NK cells. In addition, intratumoral NK cells showed impaired IFN-γ secretion, which may lead to inefficiency in DC maturation. Right image: In the tumor microenvironment of HCC, NK cells up-regulated KIR, NKG2A, PD1, TIM2, and CD96 inhibitory receptors while down-regulated NKG2D. Treg cells produced IL-10 and TGF-β. In HCC, TGFβ, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), produced by tumor-associated fibroblasts inhibit the cytotoxic activity and cytokine secretion of NK cells.