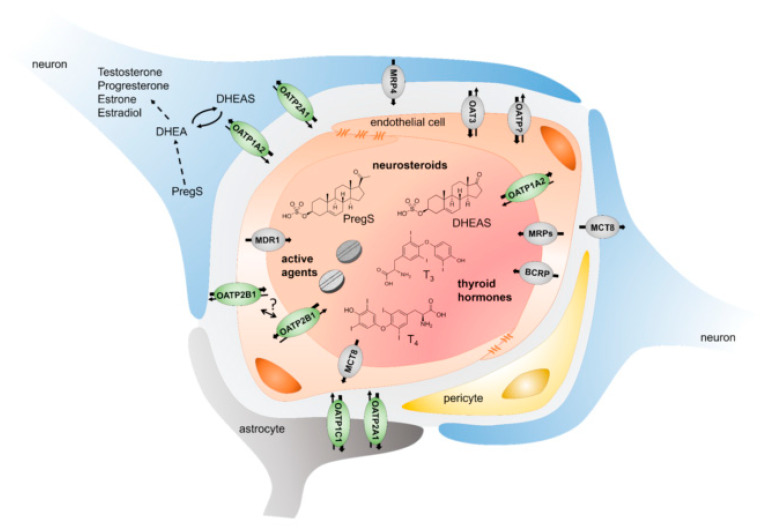
Figure 1.
Schematic depicting the current understanding of uptake and efflux transporters at the blood–brain barrier. Uptake transporters enable the brain entry of molecules of endogenous (neurosteroids and thyroid hormones) or exogenous origin. Even if data on the localization of OATPs in the endothelial cells is sparse, OATP1A2 is assumed to be located at the apical membrane, while OATP2B1 might also be found at the basal membrane. Transcellular transport as well as protection involves efflux transporters such as MDR1 (ABCB1, P-Glycoprotein, P-gp), BCRP (ABCG2), and MRPs (ABCCs). Expression of OATP transporters and efflux transporters is also found in neurons and astrocytes enabling the movement of their substrates across these membranes. Adapted from with permission from [8], Biochem. Pharm. 2021.