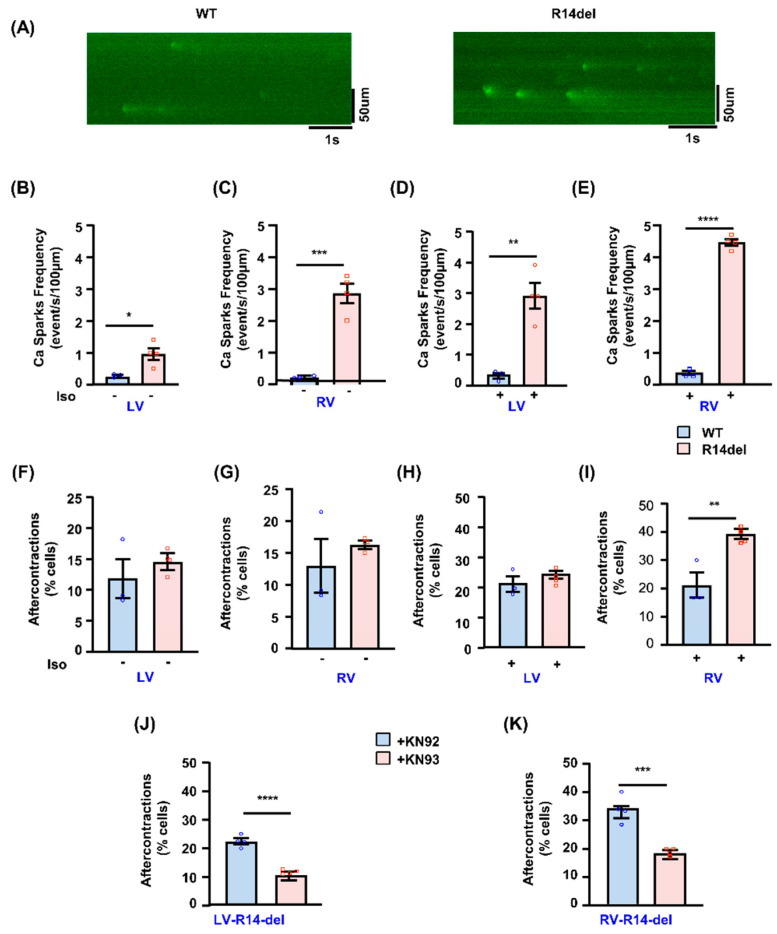
Figure 6.
Ca sparks and aftercontractions in R14de-PLN cardiomyocytes. Ca spark characteristics in isolated LV and RV myocytes. (A) Representative line-scan images of Ca sparks in RV myocytes in the presence of 100 nmol/L isoproterenol. (B,C) Mean data of Ca spark frequency under basal conditions. (D,E) Mean data of Ca spark frequency in presence of 100 nmol/L isoproterenol (Iso). n = 30 LV and 30 RV cells for WT (N = 3 hearts); n = 30 LV and 30 RV cells for R14del-PLN (N = 4 hearts). (F–I) Aftercontractions were assessed in LV and RV myocytes under field stimulation of 2 Hz and in the absence (F,G) or presence (H,I) of 1 μmol/L isoproterenol. n = 49 LV and 52 cells RV cells for WT (N = 3 hearts); n = 65 LV and 58 RV cells for R14del-PLN (N = 4 hearts). (J,K) Assessment of aftercontractions in presence of CaMKII inhibitor KN93 (1 µmol/L) or its analog KN92 (1 µmol/L) as control. n = 57 LV and 54 RV cells for WT (N = 4 hearts and n = 54 LV and 63 RV cells for R14del-PLN (N = 4 hearts). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, and statistical analyses were performed by Student’s unpaired t-test. * p ≤ 0.05 vs. WT-PLN; ** p ≤ 0.001 vs. WT-PLN; *** p ≤0.0001 vs. KN92; **** p ≤ 0.00001 vs. KN92.