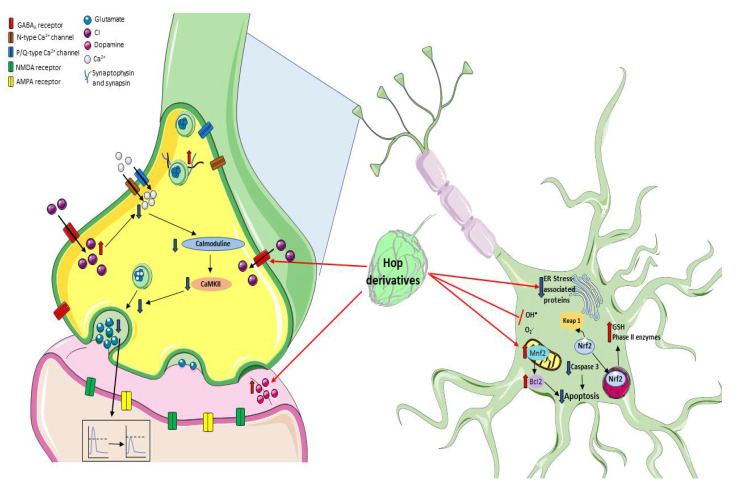
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of neuroprotection by prenylflavonoids. It has been described that prenyl flavonoids such as xanthohumol can modulate the GABAA receptors, thus increasing intracellular Cl− concentrations and reducing Ca2+ influx, leading to a decrease in glutamate release, and preventing an exacerbated excitotoxic neuronal damage. Additionally, hop metabolites can modulate the redox environment through Nrf2 signaling, regulating the expression of mitochondrial proteins, or preventing oxidative damage by directly scavenging ROS.