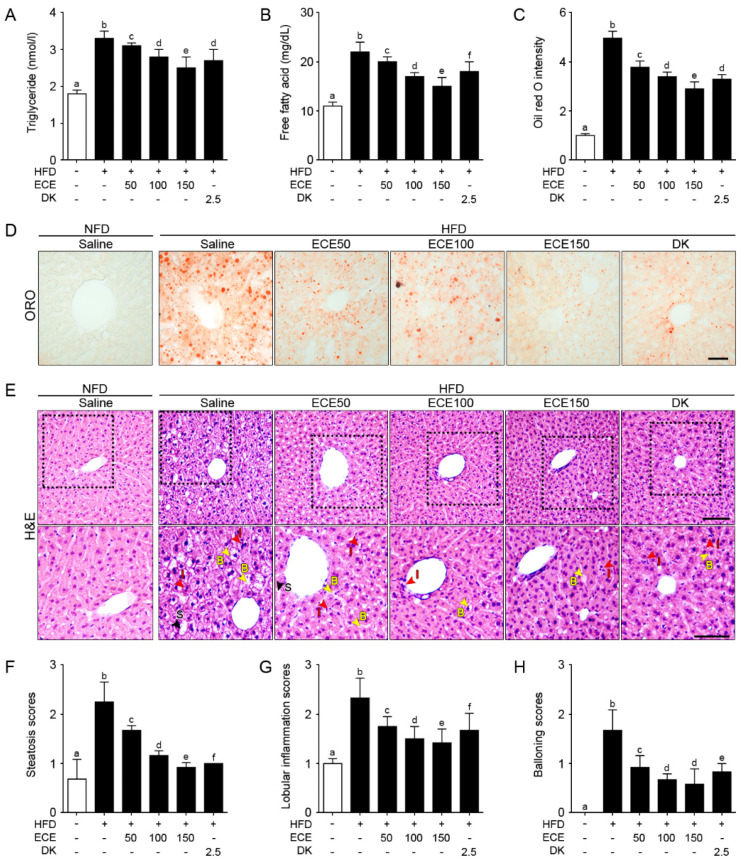
Figure 3.
Effects of ECE and DK on controlling lipid deposition and NAFLFD activity. (A and B) Triglycerides (A) and free fatty acids (B) in the liver were increased by HFD/saline and decreased by ECE or DK treatment. (C and D) The hepatic lipid deposition by ORO staining was increased by HFD/saline and decreased after treatment with ECE or DK. (E–H) The NAFLD activity was scored by H&E staining (upper row). Enlarged images (lower row) show hepatic steatosis conditions including steatosis (S; black arrows), inflammation (I; red arrows), and ballooning (B; yellow arrows) of liver (E). Quantified graphs showed that the hepatic steatosis score (F), lobular inflammation score (G), and ballooning score (H) were increased by HFD/saline and decreased after treatment with ECE or DK. Data are mean ± SD. p < 0.05, a–f; Same letters indicate nonsignificant differences between groups as determined by multiple comparison (Mann–Whitney U test). DK, dieckol; ECE, Ecklonia cava extract; HFD, high-fat diet; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin staining; ORO, oil red O staining; NFD, normal fat diet.