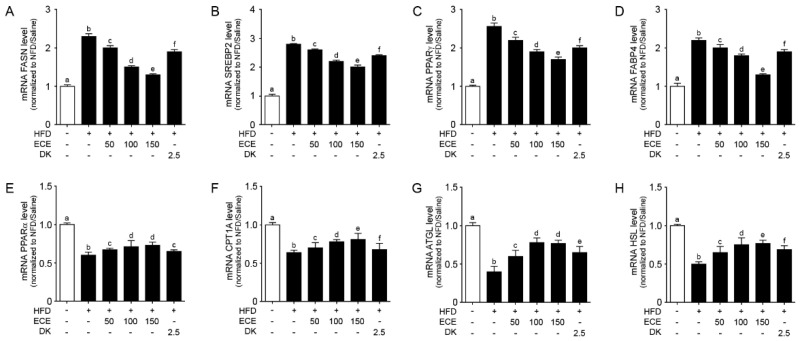
Figure 4.
Effects of regulating lipid synthesis and oxidative genes in the liver of the HFD-induced NAFLD mouse model due to the regulation of NAFLD activity. In liver tissue, (A–D) the lipogenesis related to gene mRNA levels, including FASN (A), SREBP2 (B), PPARγ (C), and FABP4 (D), were increased by HFD/saline. The addition of ECE and DK decreased those mRNA levels. (E–H) The lipolysis related to gene mRNA levels, including PPARα (E) CPT1A (F), ATGL (G), and HSL (H), were decreased by HFD/saline and decreased by ECE or DK treatment. Data are mean ± SD. p < 0.05, a–f; Same letters indicate nonsignificant differences between groups as determined by multiple comparison (Mann–Whitney U test). ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; CPT1A, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; DK, dieckol; ECE, Ecklonia cava extract; FABP4, fatty acid-binding protein 4; FASN, fatty acid synthase; HFD, high-fat diet; HSL, hormone sensitive lipase; NFD, normal fat diet; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; SREBP2, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2.