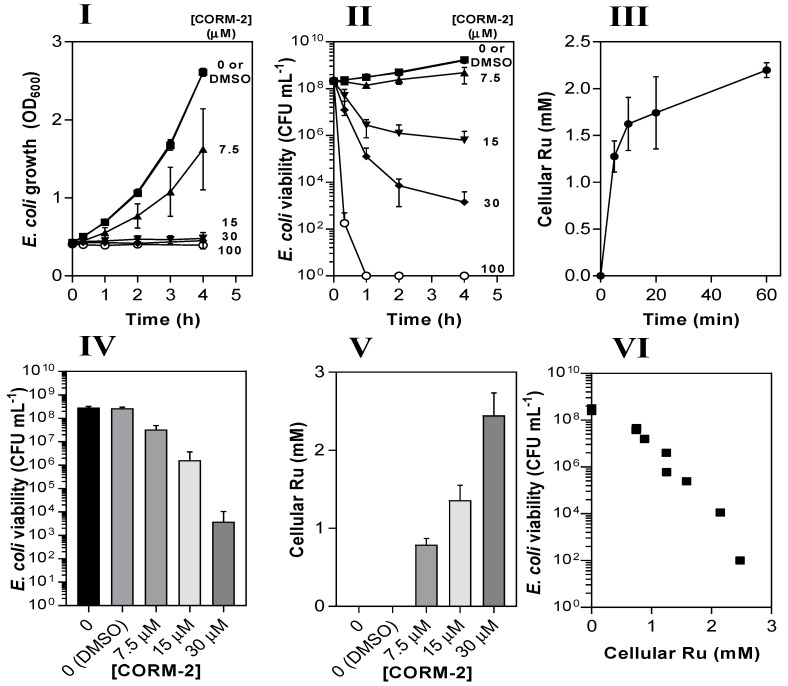
Figure 3.
The antimicrobial activity of CORM-2 against E. coli is strongly correlated with intracellular Ru accumulation. The dose-dependent inhibitory effects of CORM-2 (0–100 µM) on E. coli growth (I) and viability (II) as determined by measuring optical density (OD600) and colony-forming units (CFU). Uptake of CORM-2 (III) was assessed by measuring cellular Ru content at time intervals after addition of 30 µM CORM to early log-phase E. coli. The viability (IV) of E. coli cultures 1 h after addition of 0–30 µM CORM-2 was compared to the level of intracellular Ru (V). The data in IV and V are plotted in VI to show the negative correlation between the culture viability and the extent of Ru accumulation (r2 = 0.92). Cells were grown on GDMM in all experiments. Cellular Ru content was assessed by conducting ICP-AES on culture samples. Data represent three biological repeats ± standard deviation (SD) and the data in (VI) were analysed via a Pearson’s (two-tailed) correlational analysis (p ≤ 0.0001).