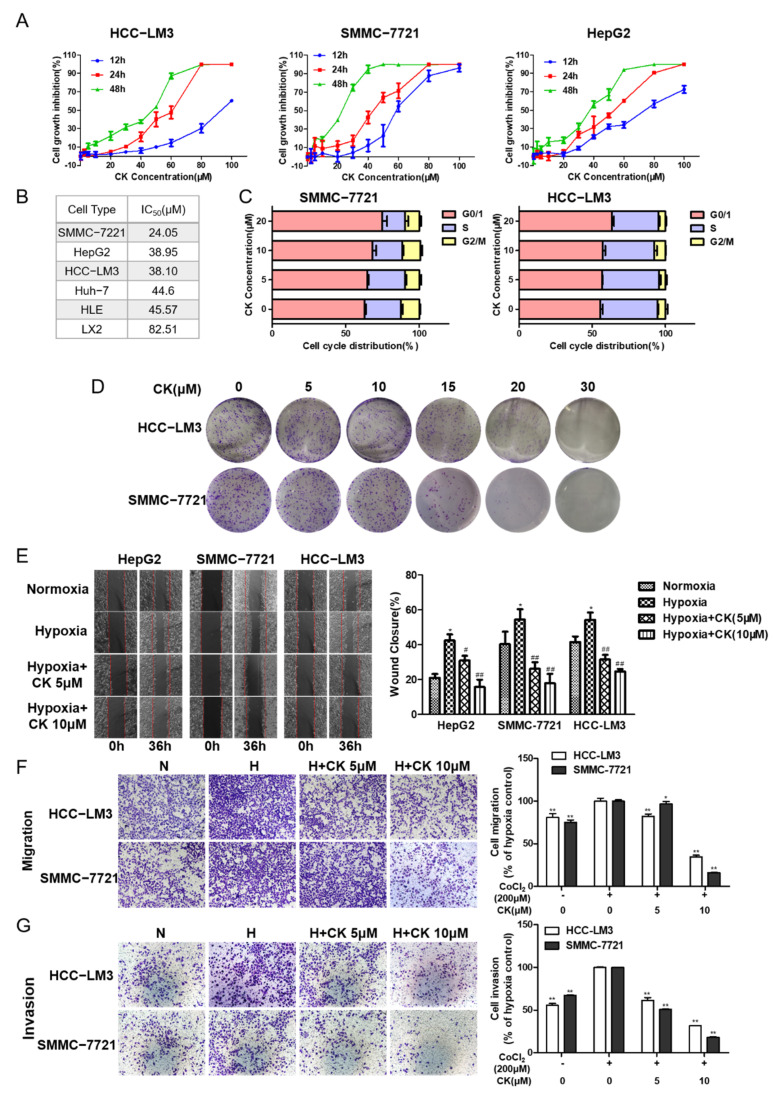
Figure 2.
Ginsenoside CK inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation and metastasis in HCC cells. (A) Cytotoxicity of ginsenoside CK treatment on HCC cell lines after 12 h to 48 h were determined by MTT assay. Figures are presented as mean ± SD of six replicates. (B) The IC50 value of ginsenoside CK on different HCC cell lines for 48 h. (C) Effect of ginsenoside CK on cell cycle distribution. HCC-LM3 and SMMC-7721 cells were treated with different concentration of CK (5, 10 and 20 μM) for 24 h. Cell cycle distribution was analyzed using PI staining assay. The data were presented as mean ± SD of three experiments. (D) Effect of ginsenoside CK on the colony formation of HCC-LM3 and SMMC-7721 cells. Representative images of colony formation were from one of three independent experiments. Effects of ginsenoside CK on metastasis potential of HCC cell lines were determined by scratch assay (E) and transwell assay (F,G). Cells were incubated under normoxia or hypoxia induced by CoCl2 and treated with different doses of CK. For the cell scratch assay, the width of wound region was evaluated 36 h after scratching by microscopy at 100× magnification. In the transwell assay, representative migratory and invaded cells were stained with crystal violet, and the data were presented as the percentage of CoCl2-treated cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. normoxia group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. hypoxia group.