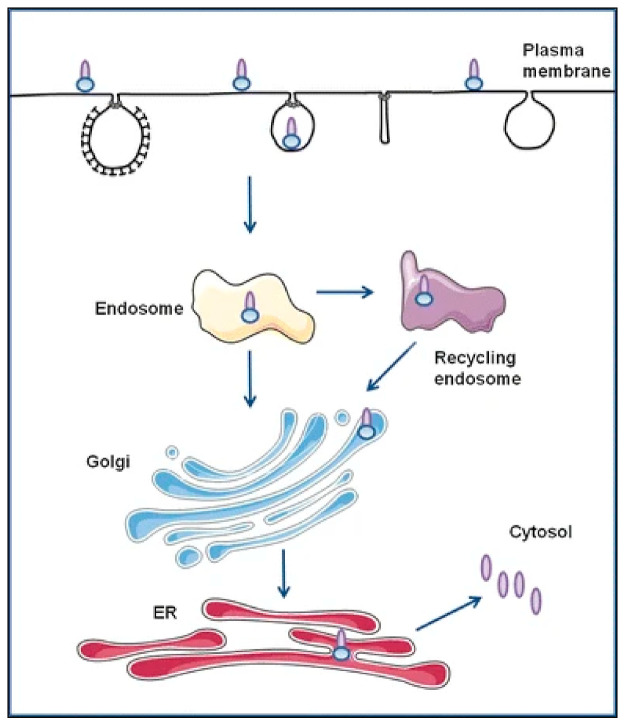
Figure 2.
Endocytosis and retrograde transport of Shiga toxin and ricin. Both toxins bind to cell surface receptors. Shiga toxin binds to the glycosphingolipid Gb3, and ricin binds to the terminal galactose of glycolipids or glycoproteins. After being endocytosed, the toxins are transported directly to the Golgi apparatus or via the recycling endosomes before they are further transported to the ER, where the A-moiety (A1-fragment for Shiga toxin) is released and translocated to the cytosol. Once in the cytosol, the active A-chain inhibits protein synthesis by removing one adenine from the 28S RNA of the 60S subunit of the ribosome. Note that recycling and transport to lysosomes are not shown. Reprinted with permission from ref. [16] Copyright 2013 Springer.