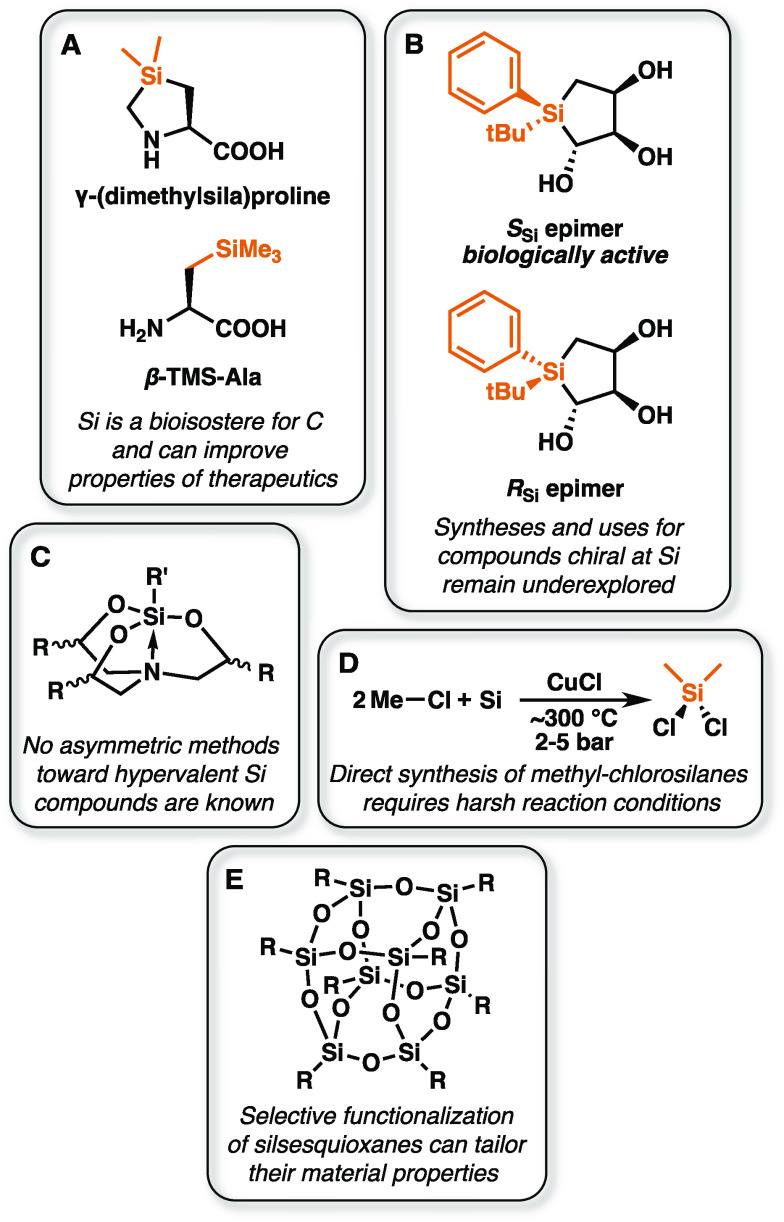
Figure 6.
Some opportunities for biocatalysis in organosilicon chemistry. (A) Silicon is a bioisostere for carbon, and substituting Si for C can be a powerful strategy for modulating the properties of pharmaceuticals and other molecules. SiAAs are a key example. (B) Molecules chiral at Si can have important biological properties but can be difficult to synthesize. The SSi epimer of silacyclopentanetriol binds the serotonin receptor 5-HT2B tightly, while the RSi epimer is inactive.85 (C) No methods for the asymmetric synthesis of hypervalent Si complexes, like silatranes, are known despite their unique properties. (D) Dimethyldichlorosilane, the key feedstock for the silicone industry, relies on energy-intensive synthetic routes.21,22 Biomethylation of silicon would present an alternative route to methylated feedstocks. (E) Silsesquioxane materials have numerous emerging applications. Enzymes may complement existing functionalization strategies.