Table 3.
Vitamins in the prevention of the muscle atrophy in vitro/vivo.
| Vitamins | Structure | Example Source | Inducer | Model | Effect | Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C |
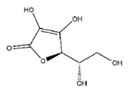
|
Kiwi fruit, lemons | Senescence marker protein-30-konckout | Mice | ↑ Physical performance | ↓ MuRF1, MAFbx ↓ Oxidative stress |
[56] |
| Vitamin D |
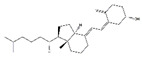
|
Milk, meat | Immobilization | C57BL/6 mice | ↑ Muscle mass | ↓ Oxidative stress ↓ MuRF1, MAFbx |
[60] |
| Vitamin E |
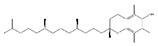
|
Soybean oil | Immobilization | Wistar rats | / | ↓ Oxidative stress | [62] |
| Aging | Human | ↑ Muscle mass/strength | / | [63] | |||
| β-Carotene |
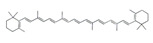
|
Carrot | Denervation | ddY mice | ↑ Muscle mass | ↓ Oxidative stress ↓ MuRF1, MAFbx, USP14, USP19 |
[65] |
| Coenzyme Q10 |
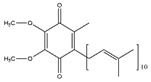
|
Sardine | Disuse | SD rats | ↑ Muscle cross section | ↑ Mitochondrial biogenesis ↓ MuRF1, MAFbx, FoxO3 |
[68] |
| Nicotinamide mononucleotide |
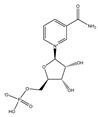
|
Broccoli, avocado | Aging | C57BL/6N | ↑ Physical performance | ↑ Mtochondrial oxidative metabolism | [70] |
Abbreviation: MAFbx, Muscle atrophy F-box; MuRF1, Muscle RING-finger protein-1; USP 14, Ubiquitin-specific processing protease 14; USP 19, Ubiquitin-specific processing protease 19; FoxO3, Forkhead box O3; ↑, Increase or promote; ↓, Decrease or inhibit.
