Table 4.
Fatty acids in the prevention of the muscle atrophy in vitro/vivo.
| Fatty Acids | Structure | Example Source | Inducer | Model | Effect | Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Docosahexaenoic acid |
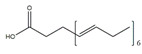
|
Fish, milk | Palmitate | C2C12 cells | ↑ Cell growth | ↑ PGC-1α, Akt ↓ Endoplasmic reticulum stress |
[71,72] |
| Oleic acid |
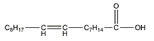
|
Sesame | Palmitate | C2C12 cells | ↑ Myotube size | ↓ TNF-α, IL6 ↓ Drp1, Fis1 ↓ Myostatin, MAFbx |
[74] |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid |
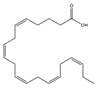
|
Fish, nut | Arthritis | Wistar rats | ↑ Muscle mass | ↑ PCNA, MyoD, myogenin ↓ MuRF1, MAFbx |
[75] |
| Arachidonic acid |

|
Pine nut | / | C2C12 cells | ↑ Cell growth | ↑ Cyclooxygenase 2 | [80] |
| Azelaic acid |
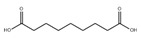
|
Oatmeal, barley | HFD | C57BL/6J mice | ↑ Muscle function | ↑ Mitochondrial biogenesis | [79] |
| / | C2C12 cells | / | ↑ Mitochondrial biogenesis, autophagy | [79] |
Abbreviation: Akt, protein kinase B; Drp 1, dynamin-related protein 1; Fis1, Mitochondrial Fission 1 Protein; HFD, high fat diet; IL-6, Interleukin-6; MAFbx, Muscle atrophy F-box; MyoD, Myogenic differentiation antigen; PCNA, Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PGC-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactiva-tor-1α; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor-α; ↑, Increase or promote; ↓, Decrease or inhibit.
