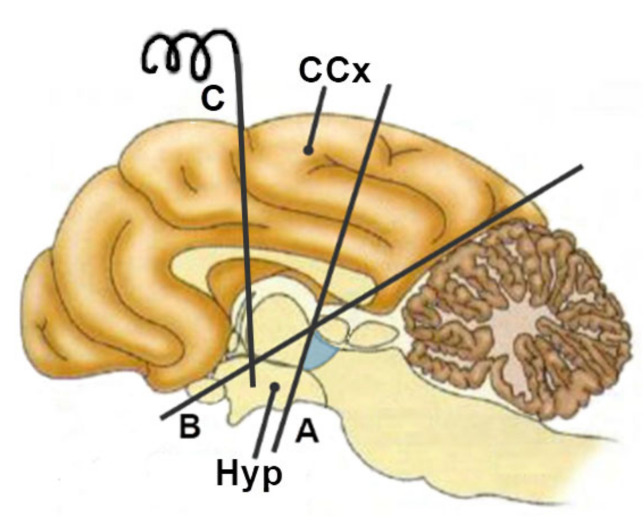
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of Bard’s experiments on cats. Behavior described as “false anger/false rage” occurs if the cutting line when decorticating a cat goes from the posterior part of the cerebral cortex through the anterior part of the hypothalamus (line marked with (B)), but not if it goes through its posterior part (line marked with (A)). In both cases, a small part of the caudoventral part of the thalamus remains preserved (marked in blue). Electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus with an electrode (without cutting) leads to anger and fear (C). The schematic follows Bard’s textual description (Bard, 1928) [35]. CCx—cerebral cortex; Hyp—hypothalamus. See text for details.