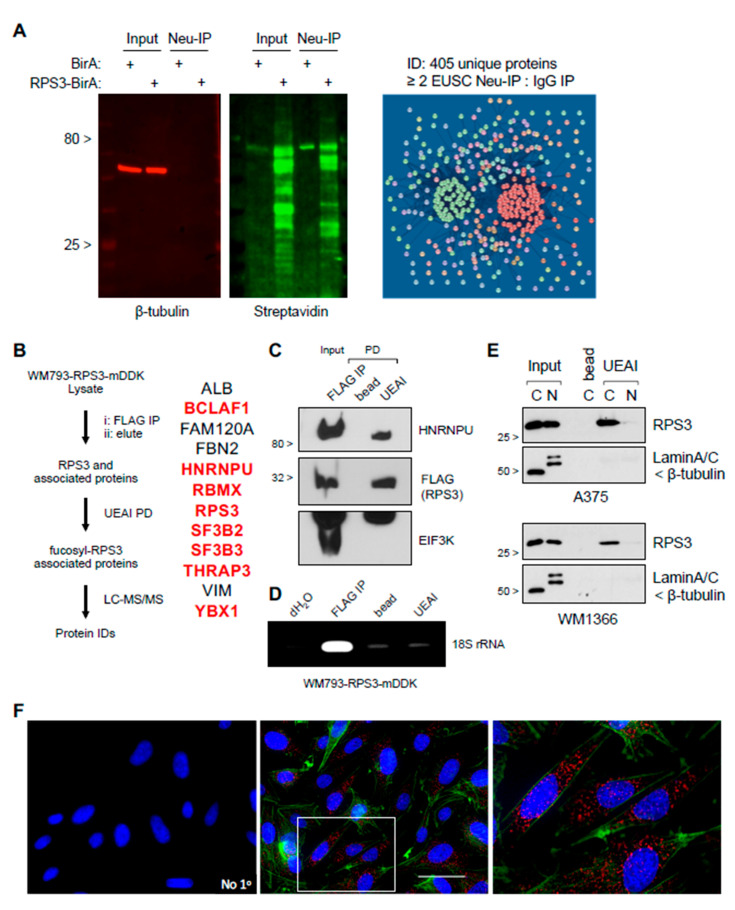
Figure 3.
Fucosylated RPS3 interacts with a ribosome-independent group of proteins associated with posttranscriptional control of RNA. (A) RPS3 BioID lysates analyzed by Western blot to show specific biotin labeling of proteins and Neu-IP capture in cells expressing RPS3-BirA versus BirA expression alone. Neu-IP captured proteins identified by LC-MS/MS analysis were found to segregate into three groups by STRING analysis: (i) ribosome-associated proteins (red), (ii) posttranscriptional RNA regulators (green), and (iii) proteins not strongly associated with either group (i) or (ii). (B) Workflow to identify proteins associated specifically with fucosylated RPS3. LC-MS/MS identified 12 proteins, a majority of which are known to interact amongst each other (highlighted in red) and posttranscriptionally regulate RNA. (C) Validation of interaction between RPS3 and HNRNPU. Analysis of FLAG IP elution of RPS3-mDDK (step 2 in panel B) and subsequent UEAI-PD for HNRNPU, FLAG (RPS3), and EIF3K (to confirm ribosome-independent interaction). (D) RNA immunoprecipitation analysis of FLAG IP elution and subsequent UEAI-PD was assessed for interaction with small ribosomal RNA (18S rRNA). (E) Cells were harvested for cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions prior to UEAI-PD to determine localization of fucosylated RPS3. Lamin A/C and β-tubulin were probed as markers for the nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction, respectively. (F) Cells were grown on glass coverslips and fixed for proximity ligation analysis (PLA) of RPS3 and UEAI lectin (Red). Cells were stained with phalloidin (Green) to visualize the cytoplasmic region and DAPI to visualize the nuclear region. PLA with no primary antibodies (No 1°) was run as a negative control. RPS3-UEAI-positive foci were found to be localized primarily to the cytoplasmic fraction.