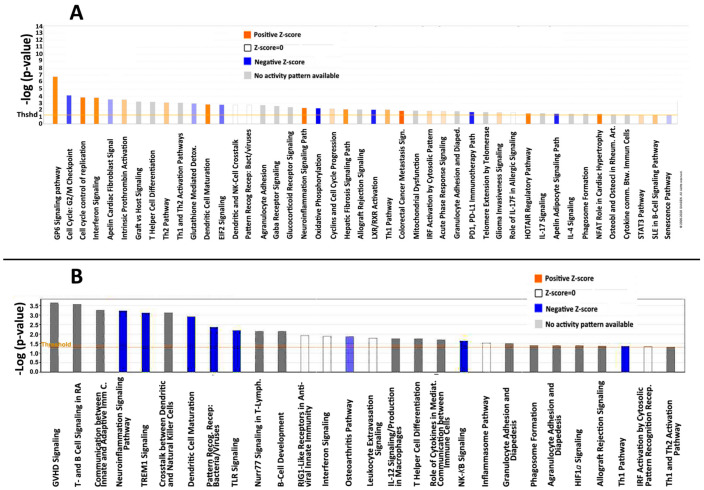
Figure 2.
Ingenuity pathway analysis of rAION responses. Pathways evaluated by Ingenuity software package (http://www.ingenuity.com (accessed on 29 August 2020)). (A) Comparison between naïve and rAION-induced, vehicle-injected ONHs. B) Comparison between rAION-induced, vehicle-injected and rAION-induced, PGJ2-treated animals. The log p-value response threshold for significance is set at 1.5 fold. Orange signal represents upregulation; blue signal represents downregulation; and white represents equivalent expression levels of pathway members altered both up- and downregulated, while grey signal represents uninterpretable (inconsistent) pathway response. In (A), comparison between naïve and vehicle gene sets reveals strong upregulation of interferon-associated pathway signaling, neuroinflammation and dendritic cell maturation pathway signaling, with moderate upregulation of components associated with both the Th1 and Th2 pathways. There is strong downregulation of the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint (=mitotic upregulation), liver-X and retinoic acid (LXR/RXR) pathway components. LXRs are inhibitors of inflammation. In (B), following PGJ2 treatment after rAION, there is suppression of the neuroinflammation, TLR and TREM-macrophage and -neutrophil signaling pathways, as well as suppression of leukocyte extravasation and Th1 signaling, but not Th2. The decrease in NF-κB signaling confirms PGJ2’s known role in suppression of this system.