Fig. 3.
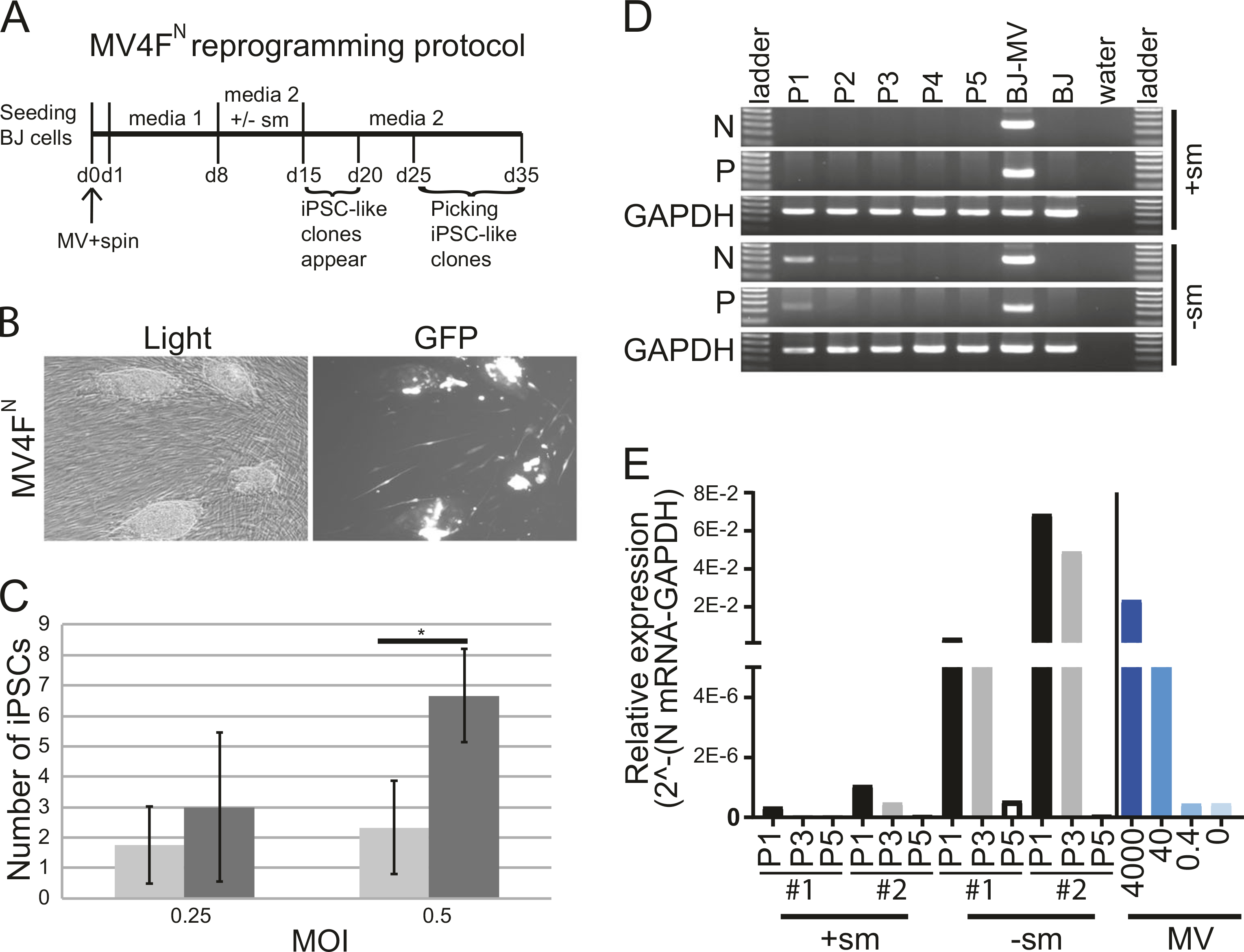
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) using MV4FN and elimination of the vector after reprogramming (a). Reprogramming schedule of human fibroblasts (BJ) transduced with MV4FN. b Representative pictures of iPSC-like clones obtained ~15 days post-transduction with MV4FN under light and fluorescence microscopy. c Reprogramming efficiency: average number of iPSC clones produced after transduction of 2.1 × 105 BJ cells with MV4FN, with (black columns) or without (gray columns) small molecules. Values and error bars reflect the mean and standard deviation of three biological replicates. *P < 0.05 with small molecules versus without small molecules, Student’s t-test. d Loss of viral gene expression after passaging. Nucleoprotein (N) and Phosphoprotein (P) mRNA expression levels were analyzed in MV4FN -derived iPSC clones by semiquantitative RT-PCR at passages 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. GAPDH is the cellular internal control, and water is the negative control. Controls: (BJ-MV) BJ cells infected with MV4FN, (BJ) BJ mock infected. e Elimination of the vector analysis. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the relative expression of the N mRNA in four iPSC clones obtained in presence ( + sm) or absence (−sm) of small molecules at passage 1, 3, and 5 (P1, P3, and P5; black, gray, and white columns, respectively). The right part of the graph (blue histograms) represents a quantitative PCR from 4000 to 0 molecules vector cDNA genome
