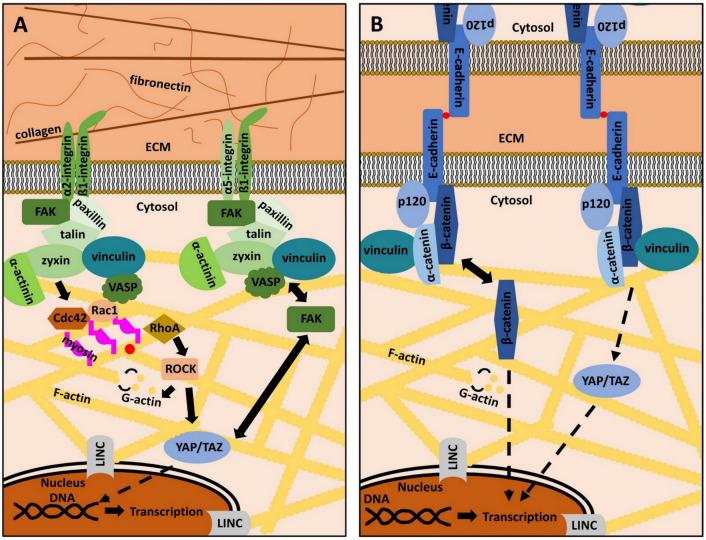
Figure 1.
The role of focal adhesions and adherens junctions in mechanotransduction. (A): Focal adhesions (FAs) are adhesion structures that bind extracellular matrix (ECM) ligands via integrin receptors. The latter are composed of varying combinations of an α- and a β-subunit. Each heterodimer has specific ECM ligands (see Table 1). Intracellularly, integrins are linked to various signaling molecules that constitute a molecular clutch, which transmits mechanical information from the ECM into the cell’s interior and vice versa. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), paxillin, talin, zyxin, vinculin, vasodilator-simulated phosphoprotein (VASP) and α-actinin are examples of important FAs proteins, connecting integrin receptors to the actin cytoskeleton (yellow). The small GTP-binding proteins Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), cell division control protein homologue 42 (Cdc42), and Ras homologue A (RhoA), together with Rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase (ROCK) modulate the dynamic de- and repolymerization of globular (G)-actin (yellow dots) and filamentous (F)-actin. FAK activity and subcellular localization of yes-associated protein (YAP) and its cellular homologue transcriptional co-activator with PDZ motif (TAZ) are strongly interconnected. The linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex couples the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton to the nucleus. Both mechanisms are important to regulate gene expression in response to mechanical signals. Details are described in the main text. (B): Cell-to-cell adhesion depends on adherens junctions (AJs). Cadherins, as exemplified by E-Cadherin, are transmembrane proteins that bind other cadherins on neighboring cells in a Ca2+-dependent manner (red dots). Intracellularly, cadherins are linked to various proteins, such as p120, α-catenin, β-catenin, and vinculin, which indirectly connect cadherins to the actin cytoskeleton (yellow). YAP/TAZ regulation is also dependent on AJs integrity. β-catenin can also serve as a transcription factor in the nucleus and its subcellular localization contributes to determining cell behavior. Further details are described in the main text.