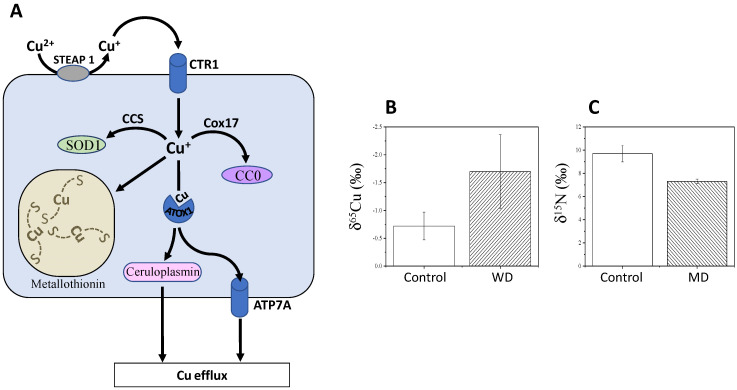
Figure 2.
Isotope fractionations in Wilson and Menkes diseases. (A) Simplified Cu utilisation, including uptake via the transporter CTR1, intracellular redistribution to various molecules including storing in metallothionein, and efflux via the transporter ATP7A (also called Menkes ATPases) or A ceruloplasmin. When copper efflux capacity is by ATP7A is insufficient, metallothionein synthesis is induced and sequesters excess copper [27]. Mutations in ATP7B (not shown here) leads to Wilson disease (WD), which is characterized by an inability to excrete Cu into the bile and therefore hepatic Cu accumulation. (B) δ65Cu values in serum of WD patients [27] and (C) hair δ15N of baby patients with Menkes disease (MD) (n = 3) compared to control (n = 18) (unpublished data). See main text for further details on Cu homeostasis. Abbreviations: ATOX1, antioxidant 1 copper chaperone; CC0, cytochrome c oxidase; SOD, superoxide dismutase. In (B,C), delta values are significantly different between patients and controls (p < 0.05).