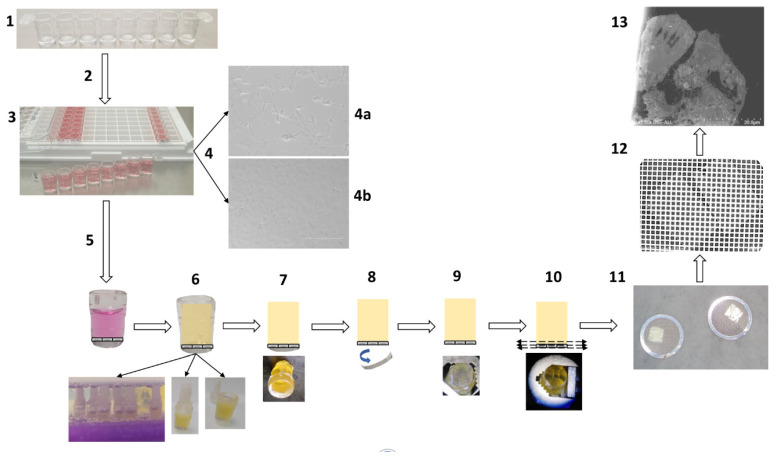
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the methodology for fast electron microscopic examination of a virus culture. (1) Removable single-break strips are UV sterilized and collagen-coated. (2) Cell culture with 200 µL suspensions of Vero E6 cells at 2 × 105 cells/mL per well. (3) Cells are virus-inoculated with 50 µL of strains or clinical sample per well. (4) Cytopathic effect detection: cytopathic effect (4a) is monitored by bright-field light microscopy, in comparison with a negative control (4b). (5) Cell fixation: cell monolayers are fixed with 2.5% final glutaraldehyde. (6) In-well resin embedding in 4 h: washes, dehydration, resin substitution and wells closed by cap sealing for microwave polymerization. (7) Plastic pruning: resin blocks are manually trimmed with a razor blade. (8) Detachment of the cell monolayer: the plastic bottom of the well is detached by cold shock via immersion in liquid nitrogen for 20 s. (9) Resin block: the resin block containing the cell monolayer at one side is ready for ultramicrotomy. (10) Ultramicrotomy: the resin block is trimmed to a pyramid and ultra-thin sections are obtained. (11) Positioning on grids: ultra-thin sections are deposited on copper/rhodium grids. (12) Contrast and metal deposition: sections are contrasted with uranyl acetate and lead citrate and grids attached to a glass slide are platinum sputter-coated. (13) Electron microscopy: electron micrographs are obtained by SEM.