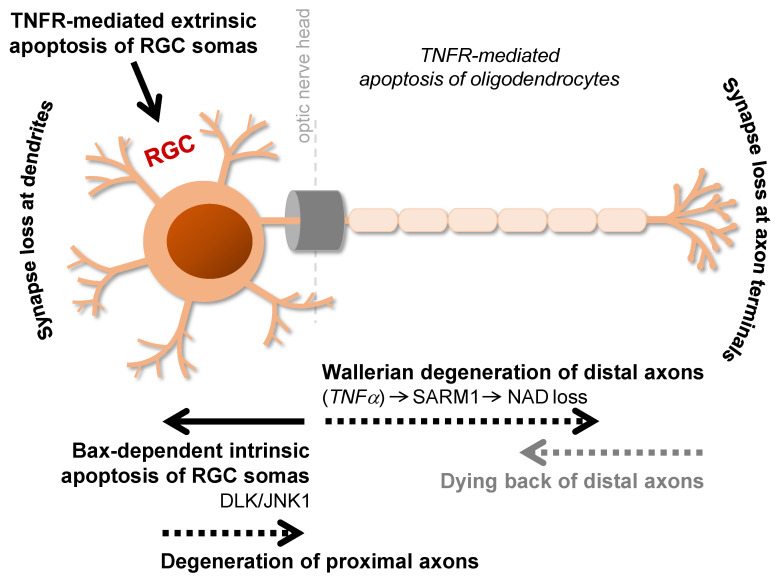
Figure 2.
Distinct molecular programs regulate somatic and axonal degeneration of RGCs in glaucoma. Glaucomatous neurodegeneration involves RGC axons, somas, and synapses at dendrites and axon terminals. Optic nerve head is a critical site of injury, and early axonal insults may originate distal and proximal signals for axonal and somatic degeneration of RGCs. A distal axonopathy is processed through Wallerian degeneration and dying back, while degeneration of proximal axons is secondary to the apoptosis of RGC somas. The apoptotic death of RGCs is processed through intrinsic/mitochondrial and extrinsic/dead receptor-mediated pathways.