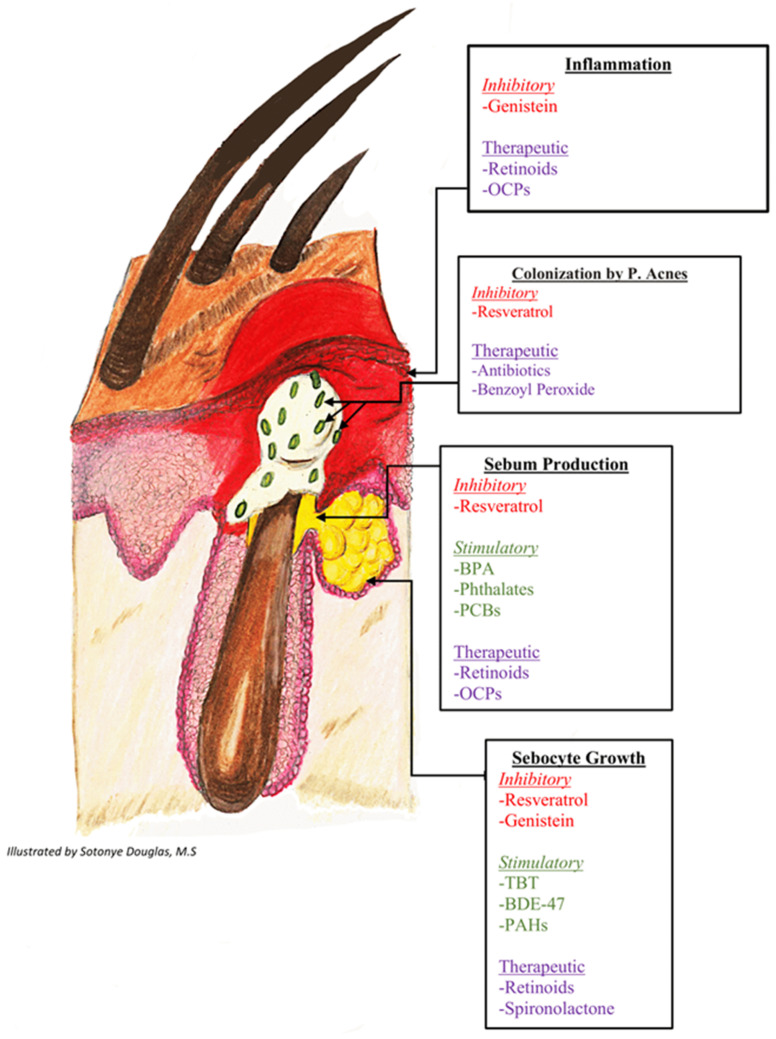
Figure 1.
Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on pathways of acne pathogenesis. 1 Genistein’s inhibitory effects are mediated by restoration of TGF-B expression and inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production. Resveratrol’s inhibitory effects are driven by downregulation of PPARy expression and inhibition of lipogenesis. 2 BPA’s stimulatory effects are driven by exacerbated cholesterol synthesis through regulation of androgen receptor target genes and direct stimulation of the glucocorticoid receptor. 3 Phthalates and PCBs’ stimulatory effects occur via decreased aromatase activity. 4 TBT, BDE-47, and PAHs’ stimulatory effects occur via altered methylation of PPARy target genes. TGF-B: Transforming growth factor-beta; BPA: bisphenol A; PPARy: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1; PCBs: polychlorinated biphenyls; TBT: Tributyltin; BDE-47: polybrominated diphenyl ether 47; PAHs: polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.