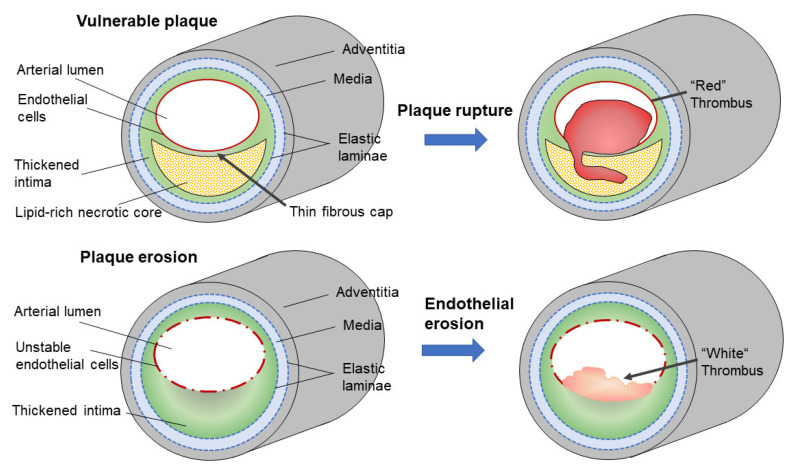
Figure 1.
Two types of culprit lesions responsible for vascular events. Vulnerable plaque is characterized by a necrotic core, which accumulates a large amount of lipids covered with a thin “fibrous cap”. Inflammatory responses render the fibrous cap fragile and lead to plaque rupture. Once the fibrous cap is broken, a rapid formation of thrombus and fibrin occurs, and a red thrombus is formed. Plaque erosion, also called superficial erosion, is characterized by a thickened intima enriched in glycosaminoglycans, but with less lipid accumulation. Inflammatory responses make the endothelial cells unstable and lead to detachment of the cells. After the endothelial cells are lost, thrombus formation occurs, and a white thrombus is formed.