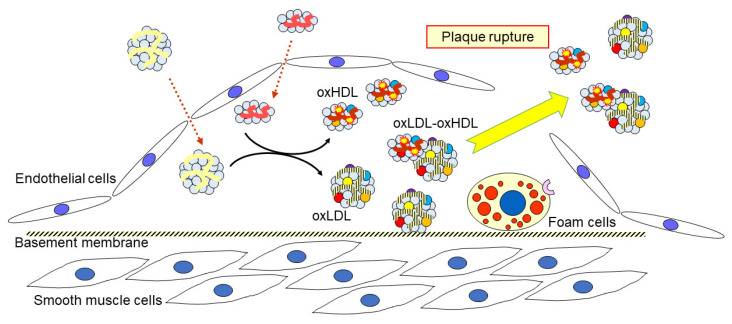
Figure 3.
A proposed behavior of oxidized lipoproteins in atherosclerotic lesions and circulation. When LDL is oxidatively modified, HDL can interact with oxLDL to attenuate oxidative modification of LDL; in turn, HDL is modified to form oxHDL. A part of oxHDL may be associated with oxLDL. These oxidatively modified lipoproteins accumulate in vulnerable plaque and are released into the circulation when the plaque ruptures.