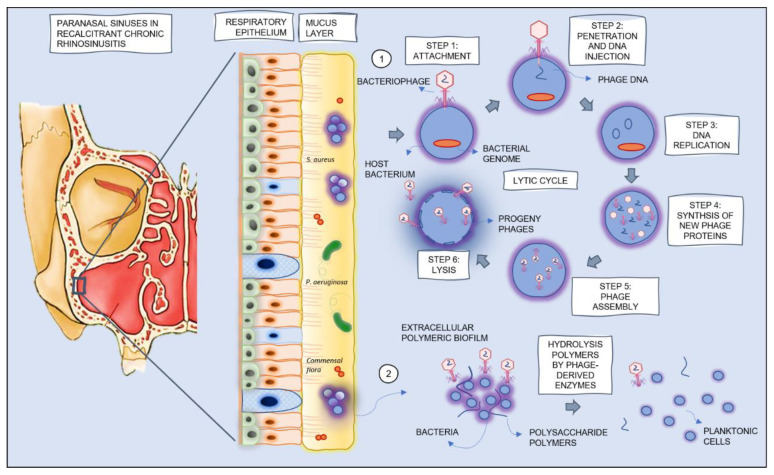
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of part of the pathophysiology of recalcitrant CRS with biofilm formation, dysbiosis, overgrowth of S. aureus or P. aeruginosa and the theoretical mechanisms of action of bacteriophages in the treatment of recalcitrant CRS: (1) lysis of bacteria during the lytic phase of bacteriophage replication and (2) reduction of biofilm mass by hydrolysis of polymers by phage-derived enzymes.