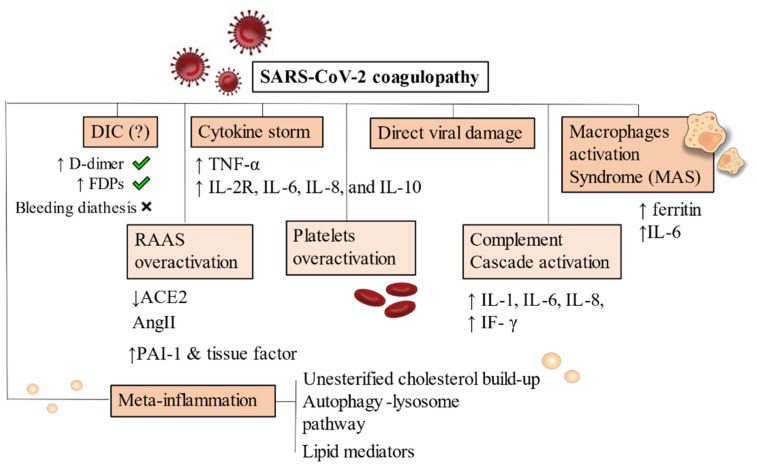
Figure 2.
Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2 coagulopathy. DIC has been frequently noticed in Covid-19 severe patients but bleeding diathesis was a less present feature. Cytokine storm and inflammatory-driven thrombogenesis is the most known hypothesis, due to IL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 cascade generation. A direct viral damage has also been acknowledged to start endothelitis and endothelial damage. MAS is instead an added mechanism present on an already compromised immune condition where hyperferritinaemia and increase in IL-6 production are pathognomonic of macrophages overactivation. RAAS system, complement and platelets also drive uncontrollable responses by generating hypercytokinemia and dysregulating fibrinolysis. Increased levels of PAI-1 and tissue factor have been demonstrated. Meta-inflammation is another possible trigger for coagulopathy. Obesity, hyperinsulinemia and metabolic syndrome are strong risk factors for severity of infection in hospitalized patients. Primary conditions developing after viral infection are depicted with a darker background. RAAS overactivation, platelets and complement activation are mainly secondary mechanisms, thus they appear in a lighter background. Abbreviations: DIC: disseminated intravascular coagulation, FDPs: fibrin degradation products, ACE: angiotensin converting enzyme, AngII: angiotensin II, PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor, IF-γ: interferon- γ, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10: interleukin 6, interleukin 8, interleukin 10. IL-2R: interleukin 2 receptor.