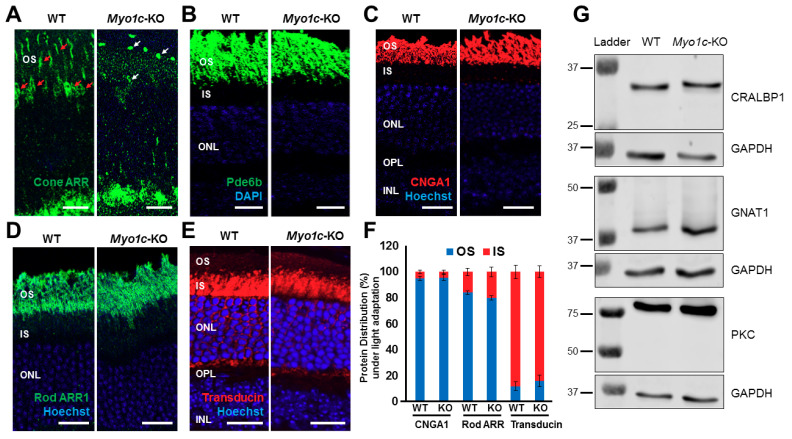
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemical analysis of protein localization in photoreceptors of wild-type (WT) and Myo1c-knockout mice retinas: Levels and localization of (A) cone arrestin (ARR), (B) Pde6b; (C) CNGA1; (D) rod Arrestin (ARR1); and (E) G-protein (transducin) were analysed in WT and Myo1c-KO mice retinas to evaluate proper protein localization to photoreceptor OS. Red Arrows in panel A highlight cone photoreceptor nuclei and OS in WT mouse retinas that were significantly reduced or shorter, respectively, in Myo1c-KO animals (white arrows in A). Images in panels A–E are representative of immunostained retinal sections (n = 5–7 sections per eye) imaged from n = 8 animals per genotype and age group (50:50 male–female ratio). Panels (A,B), mice were 2–3 months of age. Panels C–E, mice were 3–4 months of age. (F) Protein distribution (in %) of CNGA1, rod ARR1, and transducin within the photoreceptor OS and IS in light-adapted mice. For quantification of protein distribution within retinal layers, 5–7 retinal sections from each eye (n = 8 animals for each genotype) were analysed using Image J. (G) Representative Western blot (n = 3 repeats) images of retinal proteins from 3–4-month-old WT and Myo1c-KO mice (n = 2 animals per genotype) showed no significant differences in protein expression of key retinal genes among genotypes. OS, outer segments; IS, inner segments; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer.