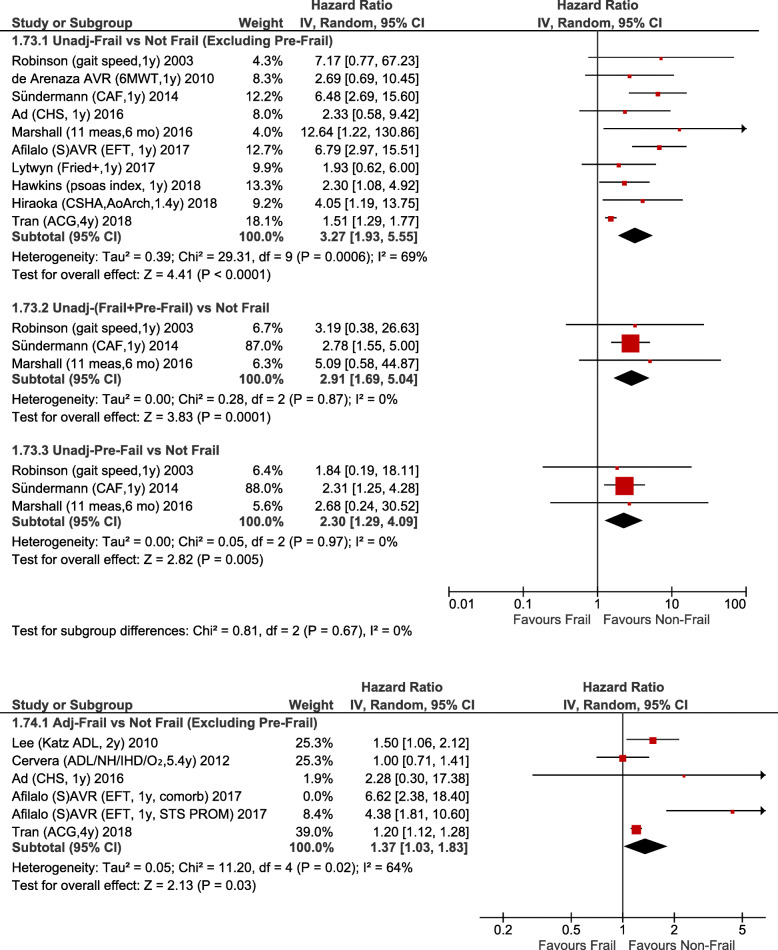
Fig. 6.
Forest Plot for mid-term mortality. Individual study and pooled unadjusted (Top) and adjusted (Bottom) hazard ratios (HRs) of frail vs non-frail patients undergoing primarily CABG and valve surgery. The pooled HRs with 95% CI were calculated using random-effects models. Afilalo et al. [21] provided two separate adjusted results; the adjusted results using the Society of Thoracic Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS PROM) were used to calculate the pooled adjusted results in the figure. If the other adjusted results using comorbidities were used (also shown in the figure) the pooled adjusted results were similar: HR1.41, 95%CI:1.02–1.96, p = 0.04; I2 = 71%. Sensitivity analyses – Risk of unadjusted long-term mortality remains higher if study with largest weighting is excluded [24]: HR3.85, 95%CI:2.63–5.64, p < 0.00001, I2 = 5%) but adjusted mid-term mortality was no longer statistically significant if study with largest weighting is excluded [24]: HR1.65, 95%CI:0.95–2.85, p = 0.07, I2 = 71%