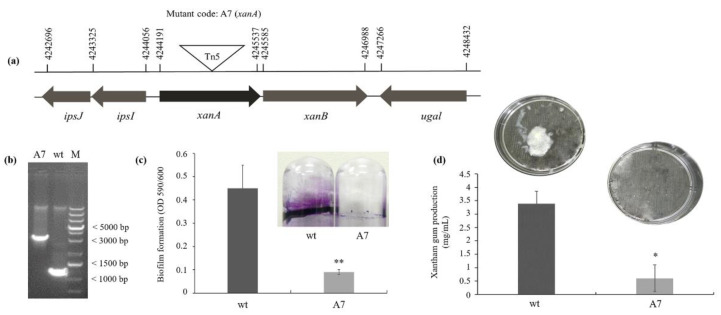
Figure 1.
Identification of the A7 mutant from an EZ-Tn5 library of X. citri by biofilm and xanthan gum assays. (a) Genetic organization of the xanA gene in the X. citri subsp. citri strain 306 genome and the lengths of the open reading and transposon insertion site in the xanA mutant are indicated. The length of each arrow represents the relative open reading frame (ORF) size and indicates the direction of transcription. The triangle indicates the Tn5 insertion site. The annotation information and sizes of the genes were obtained from the genome sequence database of X. citri strain 306 (National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI, accession No: AE008923). (b) PCR analysis confirmed the insertion of EZ-Tn5 in the xanA gene (XAC_RS18095 or XAC3579). DNA was amplified using the primers XAC3579F and XAC3579R targeting a 500-bp region surrounding xanA from the wild-type (wt) and A7 (xanA::Tn5) strains, demonstrating the increase in the length of the obtained PCR amplicon by insertion of EZ-Tn5 transposon (1.22 kb) generating a PCR product with 2.22 kb in A7 mutant. M: Thermo Scientific O’GeneRuler 1 kb Plus DNA Ladder. (c) Biofilm formation on the abiotic surface by the wt and A7 mutant strains. The values were normalized to bacterial growth (OD at 600 nm). Values are expressed as the means ± standard deviations of six biological replicates. (d) Xanthan gum production. Values are expressed as the means ± standard deviations of three biological replicates. * indicates significant difference by t-test (p < 0.05) compared with wild-type.