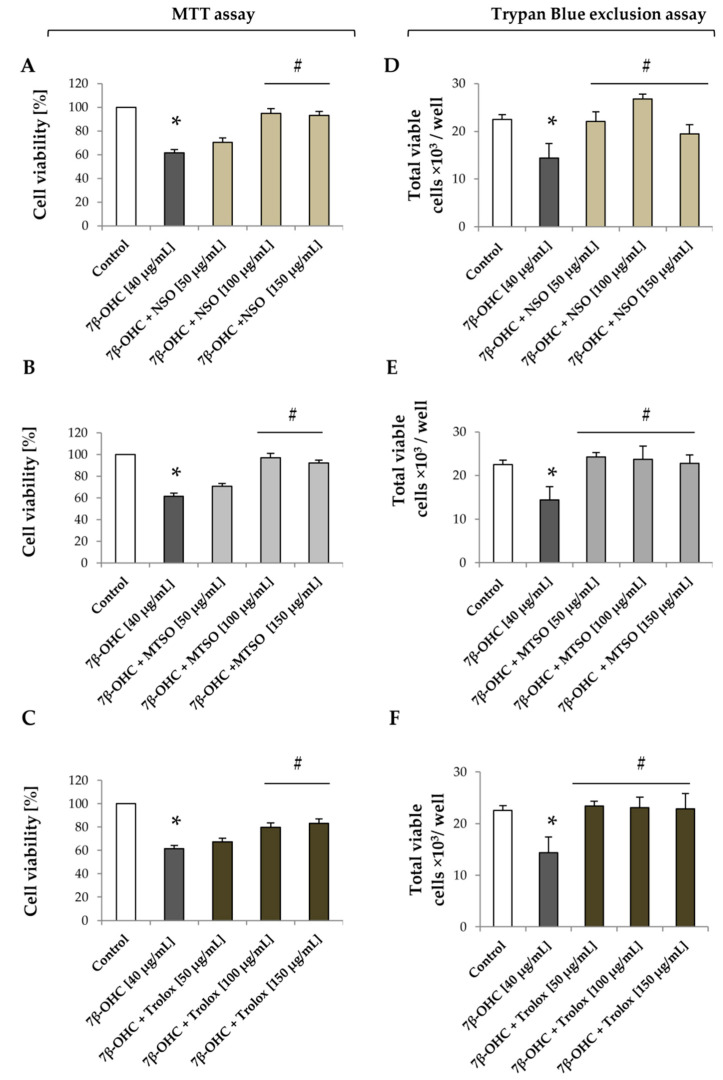
Figure 4.
Effect of NSO and MTSO associated with 7β-OHC on cell viability and proliferation. (A) effect of NSO (50–150 µg/mL) associated with 7β-OHC (40 µg/mL) on cell viability and proliferation by the MTT assay. (B) effect of MTSO (50–150 µg/mL) associated with 7β-OHC (40 µg/mL) on cell viability and proliferation by the MTT assay. (C) effect of trolox (50–150 µg/mL) associated with 7β-OHC (40 µg/mL) on cell viability and proliferation by the MTT assay. (D) effect of NSO (50–150 µg/mL) associated with 7β-OHC (40 µg/mL) on cell viability and proliferation by the trypan blue exclusion assay. (E) effect of MTSO (50–150 µg/mL) associated with 7β-OHC (40 µg/mL) on cell viability and proliferation by the trypan blue exclusion assay. (F) effect of trolox (50–150 µg/mL) associated with 7β-OHC (40 µg/mL) on cell viability and proliferation by the trypan blue exclusion assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD. 7β-OHC: 7β-hydroxycholesterol; NSO: Nigella sativa seed oil; MTSO: Milk Thistle seed oil; MTT: Methyl thiazolyldiphenyl-Tetrazolium Bromide. Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann–Whitney test or student t test. * Statistical differences were significant between the control and or 7β-OHC-treated cells (p < 0.05). # Statistical differences were significant between 7β-OHC-treated cells and 7β-OHC + (NSO or MTSO) -treated cells (p < 0.05).