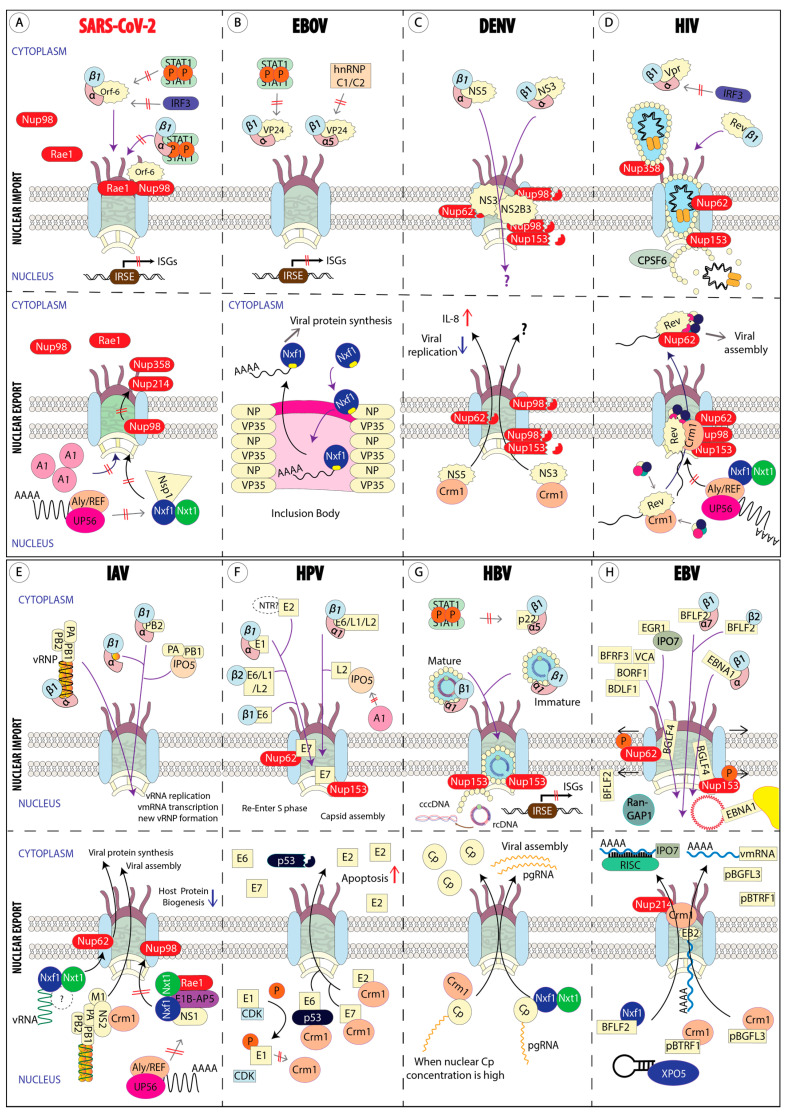
Figure 1.
Interaction between viral factors and host factors to hijack host nuclear transport machinery. (A) SARS-CoV-2 expresses Orf6 to suppress host antiviral response and Nsp1 to halt host protein biogenesis. (B) Ebola virus expresses VP24 to suppress host antiviral response. Ebola virus does not require nuclear export, but it needs the mRNA export factor, Nxf1, to mediate viral mRNA export from the inclusion body. (C) Dengue virus NS3 and NS2B3 degrade host Nups. The effect of the nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of both NS5 and NS3 in the host have yet to be elucidated. Nuclear export of Dengue NS5 is associated with elevated IL-8 production and reduced viral replication without a defined mechanism. (D) HIV capsids (yellowish balls) interact with host Nups (Nup358, Nup62, and Nup153) and CPSF6, then disassemble at an NPC basket to release PIC. HIV expresses Vpr to suppress host antiviral IFN production by blocking the nuclear translocation of activated IRF3. Nuclear import of HIV Rev is directly mediated by importin-β1. Nuclear Rev protein is needed to form a viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) transport complex to export vRNP to the cytoplasm via a Crm1-mediated pathway. (E) The Influenza-A virus nucleoprotein (NP, yellowish balls) interacts with importin-α/β1 to enter the nucleus for viral replication. Newly synthesized NPs and RdRp components (PA-PB1 and PB2) hijack host importins to enter the nucleus for new vRNP formation. IAV NS2 facilitates the nuclear export of new vRNP, whereas IAV NS1 blocks host mRNA export by forming an inhibitory complex with Nxf1. (F) HPV high-risk E6 and E7 nuclear imports induce carcinogenesis by reprogramming the cell cycle to an S-phase and promote degradation of p53. In addition, HPV viral capsid proteins (L1 and L2) exploit host importins to translocate to the nucleus for capsid assembly. Nuclear export of E2 of high-risk HPV triggers cellular apoptosis. (G) Mature HBV capsid interacts with importin-α/β1 and Nup153 to uncoat the capsid in the nuclear basket. Immature HBV capsid remains in the NPC channel after it interacts with Nup153. HBV p22 blocks the nuclear translocation of p-STAT1 to suppress host antiviral response. HBV pgRNA export is mediated either by an Nxf1-Nxt1-dependent or a Crm1-dependent pathway, depending on the nuclear Cp concentration. (H) EBV EBNA1 translocates to the nucleus to tether EBV episomal DNA on host chromosome (yellow region). EBV BGLF4 disrupts the NPC structure and promotes nuclear accumulation of RanGAP1 to promote nuclear ingress of viral proteins (VCA, BFRF3, BDLF1, and BORF1) and inhibits host classical importin-α/β1 nuclear import. EBV tegument proteins (pBTRF1 and pBGLF3) bind with Crm1 to translocate to the cytoplasm for viral tegumentation. On the other hand, EBV miRNA is carried to the cytoplasm by host Exportin-5 (XPO5) to suppress importin-7 (IPO7) translation.