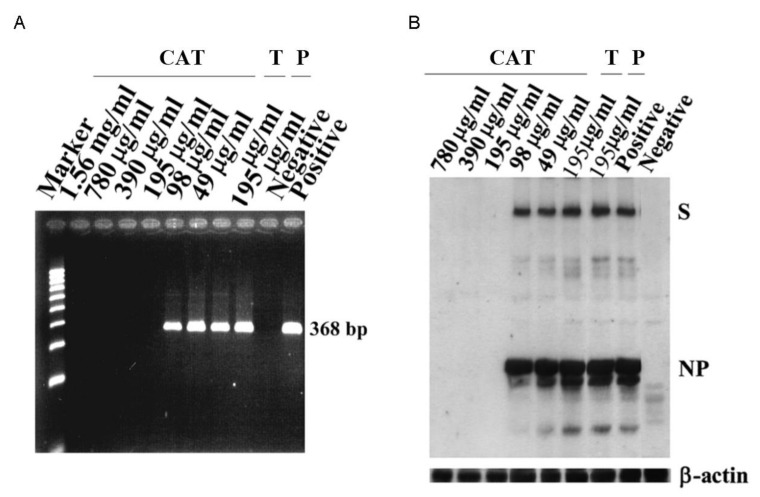
Figure 3.
The effect of catechins on SARS-CoV antigen synthesis in Vero E6 cells. The effect of catechins on decreasing the viral yields in the culture supernatants of SARS-CoV-infected Vero E6 cells (A). Viral RNA was obtained from culture supernatants of SARS-CoV-infected Vero E6 cells and analyzed by RT-PCR. PCR products of 368 bp were observed when Vero E6 was treated with catechins at 98 μg/mL and lower concentration whereas no PCR products were detected when cells were treated with catechins at higher concentrations (>195 μg/mL). The original immunoblot displays that catechins, at a concentration of 195 μg/mL or higher, completely inhibited the synthesis of viral antigens of SARS-CoV in Vero E6 cells (B). The viral antigens spikes protein (S) and nucleocapsid protein (NP) are identified. The bottom panel is an immunoblot stained with anti-β-actin antibody as an internal control. It is clearly indicated that catechins inhibited SARS-CoV budding in a dose-dependent manner. The same dose of 195 μg/mL tannin or procyanidin could not inhibit viral synthesis. Representative results from five separate experiments are shown. Positive, cells infected by SARS-CoV without catechins treatment; negative, cells without virus infection. T, tannin; P, procyanidin.