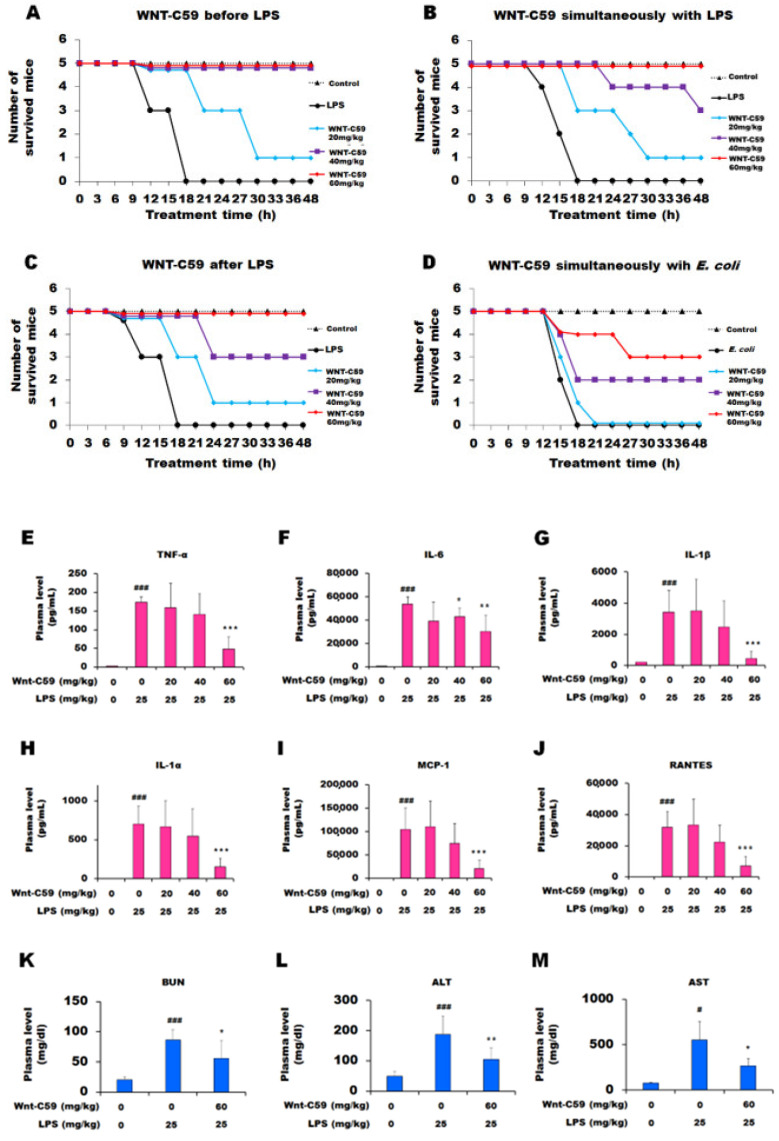
Figure 1.
Wnt-C59 reduced the lethality and plasma levels of proinflammatory cytokines and organ-damage biomarkers in endotoxemic mice. (A–D) Wnt-C59 suppressed the lethality of endotoxemic mice (n = 5). C57BL/6 mice were i. p. injected with 0, 20, 40, or 60 mg/kg of Wnt-C59 (A) 2 h before, (B) simultaneously with, or (C) 1 h after injecting 25 mg/kg of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (D) Wnt-C59 at 0, 20, 40, or 60 mg/kg was i. p. injected simultaneously with 1011 viable E. coli cells. The control group was injected with saline. (E–J) Plasma cytokine concentrations were measured using a Luminex assay (n = 7). (K–M) The levels of BUN, a kidney-damage biomarker, as well as ALT and AST, liver-damage biomarkers, were measured using a veterinary biochemistry analyzer (n = 7), respectively. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 compared with the group injected with 25 mg/kg of LPS. # p < 0.05 and ### p < 0.001 compared with the control group (unpaired t-test). LPS: lipopolysaccharide; E. coli: Escherichia coli; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase.