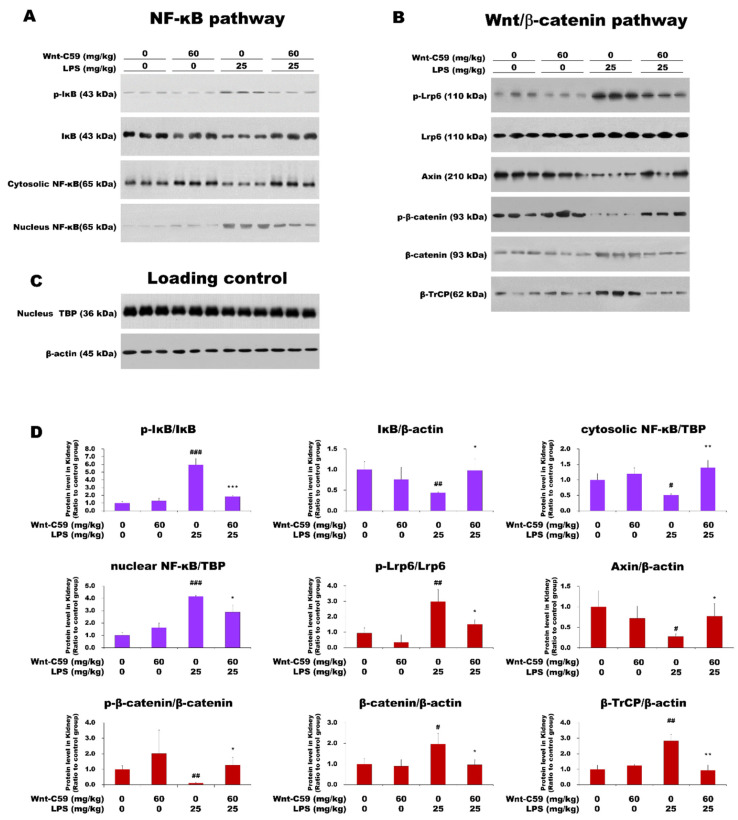
Figure 3.
Wnt-C59 suppressed both the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways in the kidney. C57BL/6 mice were i. p. injected with 0 or 60 mg/kg of Wnt-C59 and then with 0 or 25 mg/kg of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) after 2 h. (A) To measure the levels of the proteins involved in the NF-κB pathway, Western blotting was conducted using kidney protein extract from the endotoxemic mice (n = 3). (B) The levels of the proteins involved in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway were evaluated via Western blotting using kidney protein extract (n = 3). (C) β-Actin and TBP were used as loading controls for total and nuclear lysates, respectively. (D) The Western-blot band intensities of the members of the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways are shown in violet and red, respectively. The target band intensities were quantified using ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) and were normalized to the band intensities of the loading controls. The data show the average ± standard deviation (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 compared with the group injected with 25 mg/kg of LPS. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, and ### p < 0.001 compared with the control group (unpaired t-test). TBP: TATA-box–binding protein.